Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
CHOOSE THE RIGHT
DEPLOYMENT MODEL
A. Software as a Service
Software as a Service is a software distribution
and usage model that is available via a network to
the customers. Both horizontal and vertical market
software are offered by SaaS. Typical examples
of horizontal SaaS are subscription management
software, mail servers, search engines and office
suites. Examples of vertical SaaS are more spe-
cialized software such as Accounting software,
Management Information systems and Customer
Relationship Management systems.
SaaS software is leased through Service Level
Agreements (SLAs). An SLA (SLA definition,
2010) is a contractual service commitment. An
SLA is a document that describes the minimum
performance criteria a provider promises to meet
while delivering a service. It typically also sets
out the remedial action and any penalties that
will take effect if performance falls below the
promised standard. It is an essential component
of the legal contract between a service consumer
and the provider. SaaS investment is typically
limited to the subscription fee. This pricing model
provides a predictable investment that follows a
pay per usage billing scheme. Usually costs are
calculated considering user licenses, customiza-
tions costs and end user support and training costs
In this Section our goal is to clarify which services
are offered by cloud computing and how they are
related to on-premise software and system costs.
We record and analyze thoroughly all relevant
costs related to cloud deployment and in-house
development and finally suggest a three step
decision model that will support the decision of
migrating or not to the clouds.
Cloud Utilities
The main purpose of Cloud Computing is to
provide a platform to develop, test, deploy and
maintain Web-scale applications and services. A
formal definition of cloud computing is not found
in literature but most resources refer to this term
for anything that involves the delivery of hosted
services over the Internet. These services are
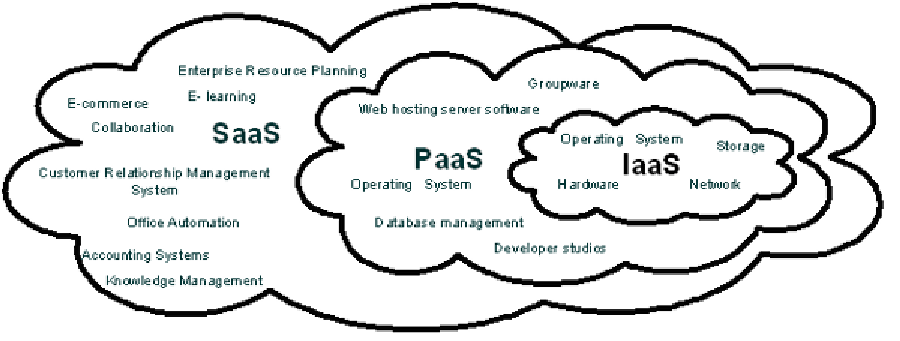
broadly divided into three categories (Dikaiakos
et al., 2009), (Lenk et al., 2009): Software-as-
a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). Figure 1
depicts the services offered by the cloud.
Figure 1. Cloud services
Search WWH ::

Custom Search