Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
An Example Event Specification for
Fire Detection Scenarios
the <DIMENSION> element. The shape or topol-
ogy of the collaboration region can be specified
by one of the following elements: <CIRCLE>,
<SQUARE>, <BALL>, <CUBE>, <HOPS>.
According to their names, these elements enable
to define 2-dimensional collaboration regions,
i.e., <CIRCLE> and <SQUARE>, as well as
3-dimensional ones, i.e., <BALL> and <CUBE>.
Rather dedicated to the topology of the WSN is
the <HOPS> element defining the collaboration
region as number of hops in a multi-hop sensor
network. If the <DIMENSION> element is omit-
ted, the 1-hop neighborhood is taken as the default
collaboration region, which is determined by
sending range. Collaboration regions are virtually
spanned around each sensor node. Each sensor
node is the centre of a collaboration region and
can be part of other collaboration regions spanned
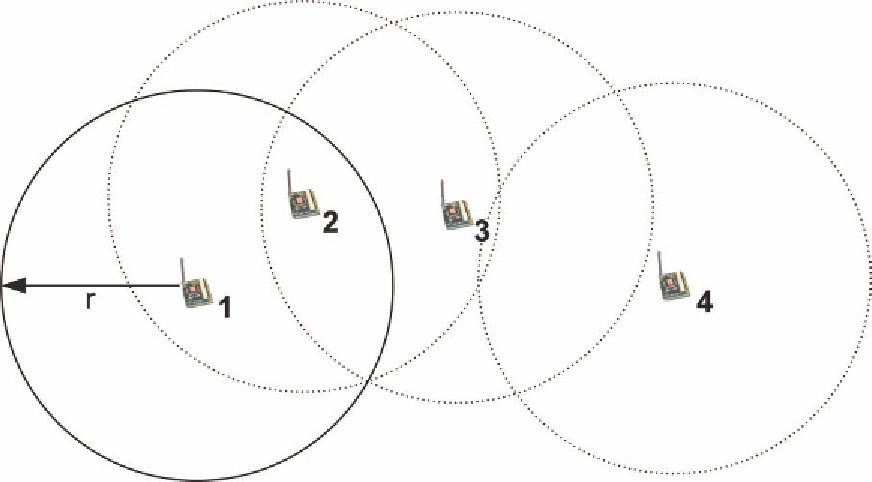
by neighboring nodes as well, see Figure 4.
Along the example of fire detection with a WSN
that is stressed throughout this chapter, we use
this section to exemplary introduce a complete
event description, illustrating ESL. Besides other
criteria, a fire can be detected by monitoring the
ambient temperature, the emission of smoke or
the existence of carbon monoxide. Traditional and
widely used fire detectors set off a fire alarm if
monitored smoke or carbon monoxide emissions
exceed a given threshold. Also changes in tem-
perature can be analyzed to indicate or even detect
a fire. In spite of using well-engineered sensing
devices these methods are still vulnerable to false
alarms, e.g., triggered by smoking, burnt food or
influences of various heat sources. Each detection
method is suitable to detect fires indeed, but proper
fusion of all systems enhances the reliability of
detection and decreases the false alarm probabil-
Figure 4. Example deployment of nodes with circular collaboration regions configured by radius r.
Whereas node 4 is isolated, node 1 shares its event region with node 2, node 2 may collaborate with 1
and 3 and 3 may evaluate events with node 2.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search