Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
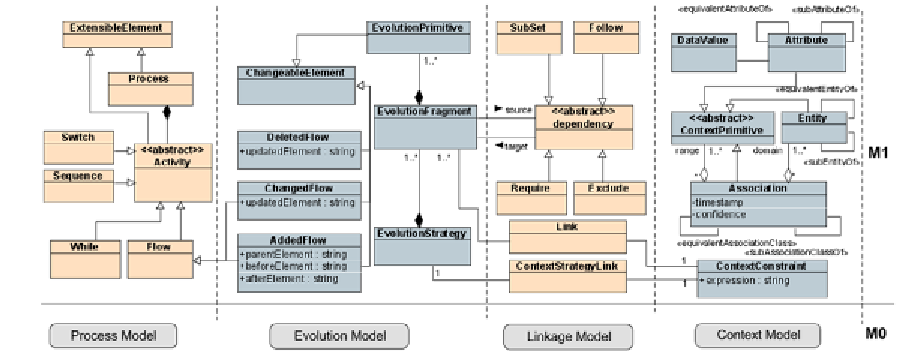
Figure 4. The conceptual model for context-aware adaptation
A Conceptual Model for
Context-Aware Adaptation
edge is the
ContextPrimitive
which represents
the base context constructs (primitives): entity
classes, entity attributes and entities associations.
Apto
adopts MDD methodology whose primary
objectives are: portability, interoperability and
reusability. The proposed conceptual model is
structured in four main sections that address,
respectively, the modeling of the service-based
process, context, evolution, and linkage between
evolution and context models (see Figure 4).
•
Entity class:
represents a group of entities
(e.g. users, places, devices, etc) sharing
some properties.
•
Attribute class:
represents an entity's at-
tributes e.g. preference, position, tempera-
ture, etc.
•
Association class:
represents a relation-
ship between one entity and either another
entity or an attribute.
Basic Process Model
In
Apto
we denote the original process as a basic
process. This can be either an existing process
model or a newly created one. The basic process
could be defined for the most frequently executed
variant of a process family, but this is not a require-
ment. We use a UML process definition model. For
illustration purposes, Figure 4 depicts some of the
main meta-classes representing the key elements
of BPEL process model, and their relationships.
Further optional modeling constructs are addi-
tional facts about the entities and attributes. These
are: specialization and equivalence relationships
that may be specified between two entity classes,
two attribute classes, or two association classes.
In addition, we introduce the context-dependent
constraint concept which allows us to specify
conditions that must hold to introduce some kind
of context-aware adaptation by specifying the
evolution fragments that should be applied to the
process as described in the next sections.
Context Model
As in previous work (Jaroucheh et al. Feb 2010)
the main construct for representing context knowl-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search