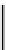Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
IP
LP
CP
n
CLK
SE
Scan in pattern i+1
Scan out response i
Scan in pattern I
Scan out response i-1
Fig. 3.10
Timing diagram for two pattern tests using LOS test application method
seen that SE has to change fast before the capture cycle. This implies that the SE net
must be designed similar to a clock network since it is also distributed to all the scan
cells (flip-flops). In LOC method SE has to switch after the initialization cycle and
this can happen as slowly as needed by, for example, introducing some idle cycles
after the initialization phase. In at-speed test the capture cycle, also referred to as
a fast capture cycle, is applied after one clock period of the desired frequency of
operation.
In practice, the following advantages and disadvantages of the LOS and LOC
test methods have been observed. Test generation times and test set sizes for LOS
method are much smaller and achievable fault coverage is higher compared to that
for LOC method. Additionally, when multiple scan chains are used as is typical in
large industrial designs to reduce test application time, fault coverage using LOS
tests increases compared to using a single scan chain (
Pomeranz et al.
2002
)
. Fault
coverage using LOC tests is independent of the number of scan chains used. How-
ever design effort to insure that SE can switch state fast is higher while a fast SE
is not needed for LOC test method. LOC tests are often preferred since they are
“closer” to the normal functional operation. It should be noted that in one scan de-
sign method called Level Sensitive Scan Design (LSSD)
(
Eichelberger et al.
1978
)
all scan chain control signals are designed as clocks and hence both LOS and LOC
test methods can be used without any additional design effort. Both methods achieve
lower fault coverage than if arbitrary two-pattern tests are applicable, for example
using enhanced scan (
Dasgupta et al.
1981
) that has a three latch scan cell to enable
storing both patterns of a two pattern test. However using enhanced scan that adds
extra hardware overhead may not be acceptable for many designs.
3.1.5
Non-enumerative Procedures and Path Selection Methods
Since the number of paths in a realistic design could be extremely large and so could
be the number of tests to detect all detectable path delays, several methods have
been developed to address these issues. In order to reduce the impact of the size of