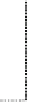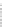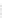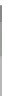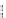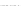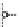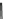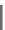Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
a
V
A
b
V
D
I
b
V
B
V
B
V
C
V
A
V
D
V
E
V
G
V
F
I
b
R
b
R
b
I
d
V
C
V
G
I
d
V
E
V
F
c
d
I
b
V
A
V
D
V
B
V
B
V
C
V
C
V
A
V
D
V
E
V
E
V
G
V
F
V
G
V
F
R
b
R
b
I
b
I
d
I
d
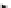
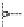
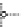
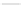
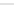
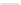
Fig. 2.26
Bridging fault with downstream current. (
a
) Gate level and (
b
) both pMOS transistors
on (NAND gate), (
c
) one pMOS transistor on (
d
) nMOS network on (NAND gate)
In order to evaluate the impact of the downstream current, let us consider the
is driving, in turn, a NAND gate. When the bridge is activated, the current flowing
through V
D
and V
E
generates the bridge current. Due to voltage degradation on V
E
,
there may be also downstream current flowing through the NAND gate provided
that V
F
is set to logic 1. The three possible network excitations in the presence of
The magnitude of the downstream current depends on different factors, namely:
the bridged networks, the topology of the downstream gate and the bridge resistance.
The relationship between the downstream current and the voltage of the bridged
node is similar to the current behaviour in the presence of a floating node caused by
an interconnect full open. If an intermediate voltage value is induced between V
Tn
and (V
DD
V
Tp
), downstream current is generated. The amount of current depends
Neglecting the downstream current, the current signatures for the examples in
the V
F
value. If V
F
is set to logic 0, there is not downstream current. In this case,
logic 1, there is downstream current, which increases the total current caused by the
bridge. In this sense, every of three upper current levels may unfold into two sub-
since seven current levels are now reported.
stream current that consists in decreasing V
DD
, to the point that the downstream
current becomes negligible and the bridge current (I
b
) is practically equal to the