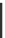Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
EO
2
EO
3
EO
4
EO
5
EO
6
A (0/1)
B (0/1)
C (0/1)
A (1/0)
B (1/0)
C (1/0)
a
b
G1
G2
S
1
S
3
G1
G3
S
2
S
4
S
5
G4
G2
G3
G4
Fig. 1.23
Segment fault model (
Huang
2002
)
. (
a
) Target net driving three gates and (
b
)segment
division according to layout information
In a subsequent work,
Liu et al.
(
2002
) presented a model-free diagnosis
algorithm for multiple interconnect open faults. In the presence of an open fault,
this procedure considered the worst case scenario. Each fan-out branch of the stem
was assumed to behave randomly, that is, independent of the value on the stem.
Hence, every branch could take an arbitrary logic 1 or 0 for each test pattern. An
iterative algorithm using X values identified possible faulty locations. Subsequently,
simulations were carried out to reduce the set of candidates.
Unlike these previous works, some recent studies have considered physical in-
procedure using the segment fault model. A segment .S
i
/ is a part of a net based
on routing information. By knowing the layout, the target net can be divided into
open segments on the target line. The main drawback of this methodology is that
there are cases where segments are still too long and the open cannot be precisely
located along the line.
In the work by
Sato et al.
(
2002
), a technique to find open vias by using physical
information was proposed. The capacitances between the floating net and its neigh-
boring lines were taken into account to predict changes in the floating node voltage
C
1
.P /
C
0
.P /
C
C
1
.P /
E.P /
D
(1.9)
C
1
.P/ is the sum of the capacitances between the floating net and coupled structures
tied to logic 1 for a specific test pattern, and C
0
.P/ stands for the sum of the ca-
pacitances between the floating net and its coupled structures set to logic 0 for the
same P pattern. The patterns exciting the fault are divided into two sets:
0
and
1
,
where
0
.
1
/ is composed of patterns which set the floating net voltage to a value