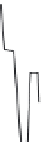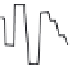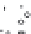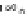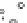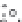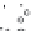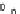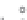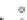Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
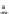
Fluvial Terraces
gravel cap
on strath
Fill 1
Fill 2
Fill 3
Aggradational
terraces
A (ii)
A (ii)
Degradational
terraces
Paired
terraces
Unpaired
terraces
B (ii)
B (ii)
aggradational
terrace 1
cut-and-fill history
aggradational
terrace 2
strath terrace
aggradational
terrace 3
incision
aggradation
degradational
terraces
Fill 1
C
Fill 2
Fill 3
time
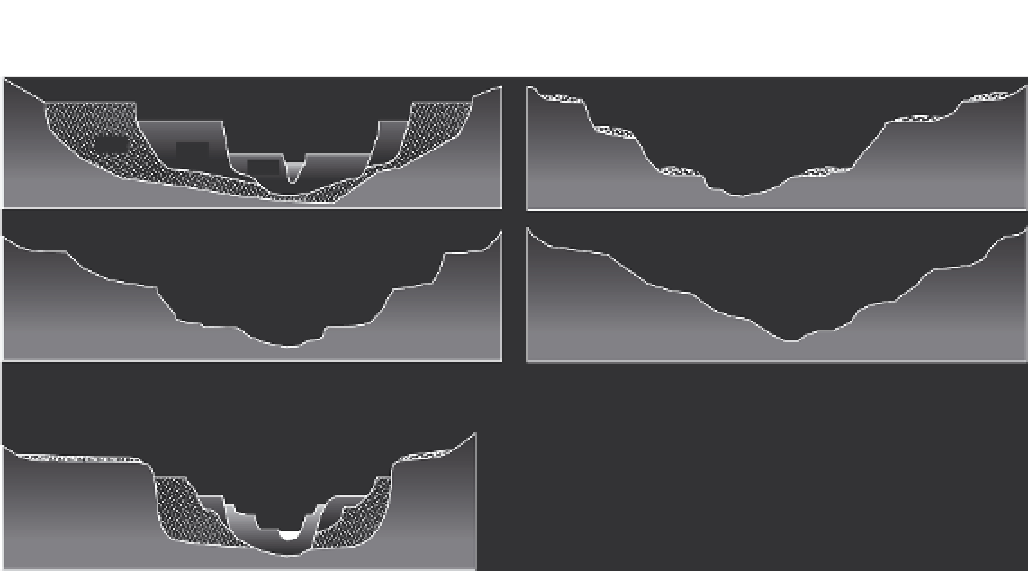
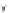
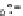
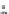
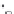
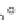
Fig. 2.11
Schematic configurations of river terraces.
A. Cross-sectional sketches of (i) aggradational and (ii) degradational fluvial terraces. B. (i) Paired and (ii) unpaired
river terraces. C. Cross-section showing complex sequence of aggradational and degradational surfaces. Multiple
cut-and-fill events are outlined in the right-hand box.
Bedrock Incision Model
incise bedrock
bevel strath 1
incise bedrock
bevel strath 2
incise bedrock
A
Fill & Bevel Model
aggrade
b
e
vel strath
1
incise fill
bevel strath 2
incise fill
B
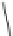
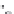
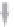
Fig. 2.12
Models for formation of strath terraces.
A. Traditional bedrock incision model for strath terrace formation results from extensive lateral beveling by a river,
causing a broadening of the valley floor and retreat of the valley walls. Intervals of strath cutting are separated by
intervals of river downcutting through the bedrock. Height of a strath above the bedrock valley floor indicates how
much bedrock incision has occurred since strath formation. B. Fill-and-bevel model (e.g., Hancock and Anderson, 2002)
occurs within a valley already incised into the bedrock. Aggradation within the valley protects the bedrock valley floor
from erosion, but enables the river to attack the valley walls above the bedrock floor, where new straths are then cut.
If the river subsequently incises partway through its fill, new straths at a lower level can be cut. Note that the height of
the strath above the bedrock valley floor is unrelated to the amount of bedrock incision since the strath formed.
Although the geometry of the straths for the two models is identical, strong contrasts exist in the volume of bedrock
that must be removed during strath formation and in the strath's relationship to the history of bedrock incision.