Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
x
= 0
x
= 5
12
10
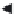
Design space
8
32
6
24
y
= 4
4
16
All possible
objective functions
min
2
0
6
0
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
x
Figure 7.1
Graph of objective function and its solution.
L
D
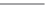
Figure 7.2
Cylinder model.
The volume it contains is given by
2
π
D
fDL
o
(,)
2
L
4
The next thing is to determine the
constraints
. What are the minimum and maximum values
of the parameters? Which, if any, of the parameters are fixed? If we go back to our design
concepts these limits give us the boundaries of the design space. We will then be looking for
an objective: Are we trying to minimize mass for a fixed volume? Are we trying to maximize
volume for a fixed mass? We need to know what we are looking for, but we also need to know
a tolerance. We will never find an exact solution but we may find one if we state we are looking
to find a solution where the mass is minimized but the volume should be 0.995-1.005 liter.
In graphical terms this is like plotting the design space as a surface and using the objective
function to determine a solution, as illustrated in
Figure 7.3
.















Search WWH ::

Custom Search