Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
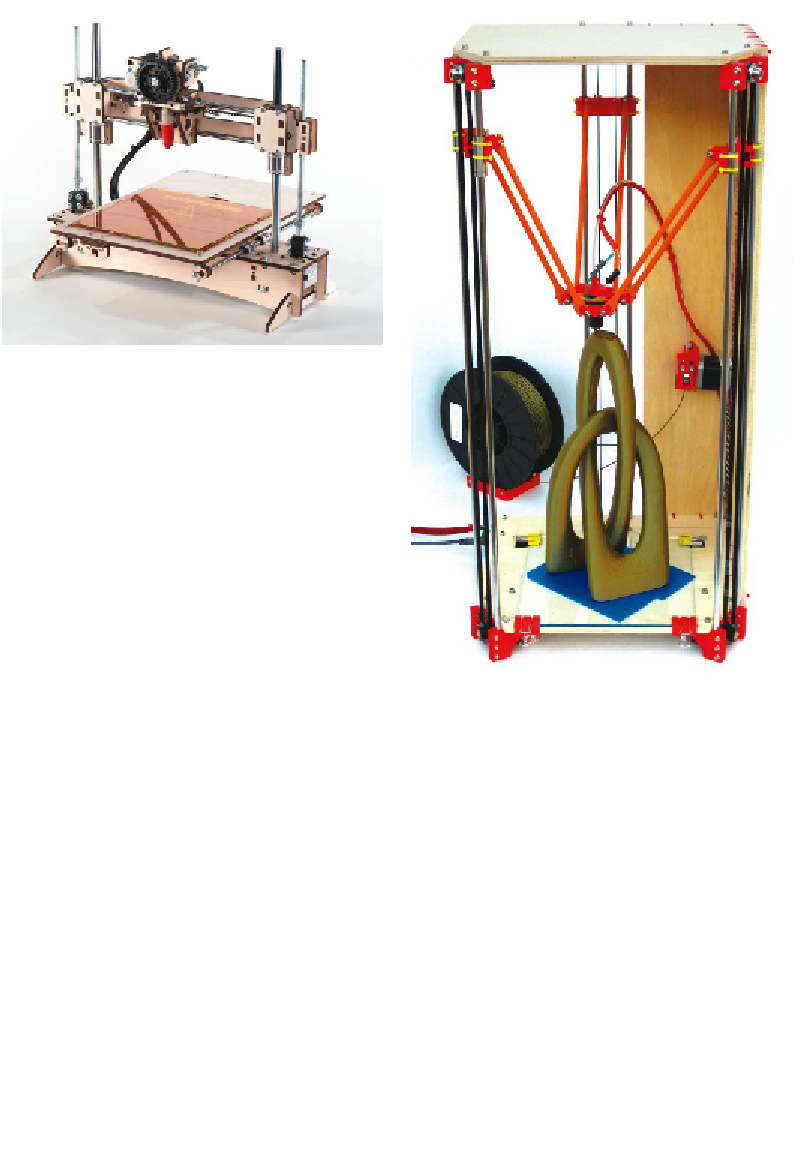
Figure 1-3.
A Printrbot
Deltabot
Industrial pick-and-place robots typical-
ly use this design. A deltabot has three
control rods connected to the toolhead,
and these rods can be moved to control
the position of the head. Recently, Jo-
hann Rocholl adapted this technology
to 3D printing and created the Rostock
(
Figure 1-4
). Hard to explain, it looks like
an alien probe is printing your favorite
model.
The Rostock printers (so far) use a Bow-
den setup to separate the hot-end from
the extruder, allowing for very quick and
precise head positioning with relative
mechanical simplicity. The downside is
increased complexity in the driver; the
hot-end positioning is not a linear set of
steps because of the non-linearity of the
motion between the vertical axis and
the planar positioning of the hot-end.
Figure 1-4.
The Rostock
3D Printer Parts
Print bed
This is the bed upon which the printed
part rests during production. Bed tem-
peratures can be ambient or heated. A
non-heated bed is often covered in
painter's tape, as seen in the Ultimaker
(
Figure 1-1
), to which the printed mate-
rial adheres. Heated beds, as seen in the
Printrbot (
Figure 1-3
), keep the part
warm during the print and prevent
warping. Depending on the material, a
heated bed will maintain a temperature
from 40°C to 110°C throughout the print.