Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
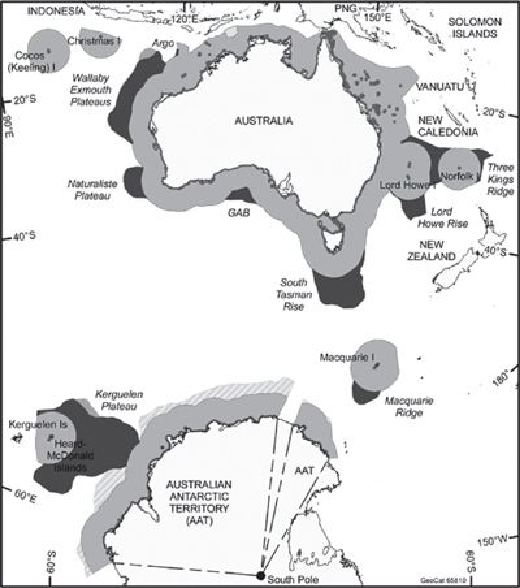
The sovereign rights of coastal states and the common heritage rights of the international
community do not sit easily with one another. The submissions produced by coastal states
are expensive and time-consuming. The CLCS is a small body and has a huge backlog
of submissions to evaluate. It is conservatively estimated that it will take the CLCS some
40-50 years to clear the current waiting list. If, as the United States thinks, there are no
coastal states in the Antarctic region, then the waters adjacent to the polar continent would
be part of what is termed 'the area'; thus they would be deemed to be part of the com-
mon heritage of the international community. Offshore jurisdictional claims in the Antarc-
tic are potentially explosive because they unsettle the existing position of non-recognition
of the United States, Russia, and new members such as China and India. It must be noted,
however, that the US Senate has yet to ratify UNCLOS despite successive presidents, both
Democrat and Republican, urging ratification.