Java Reference
In-Depth Information
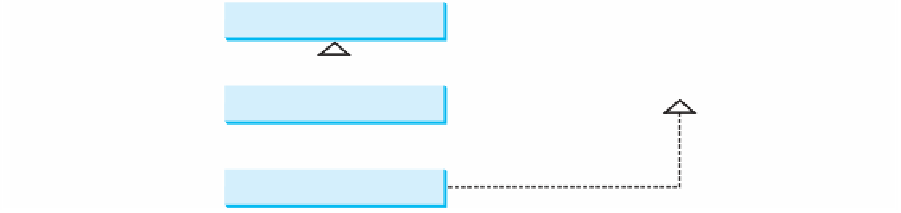
GeometricObject
«interface»
Notation:
The interface name and the
method names are italicized.
The dashed lines and hollow
triangles are used to point to
the interface.
java.lang.Comparable<ComparableRectangle>
+compareTo(o: ComparableRectangle): int
Rectangle
ComparableRectangle
F
IGURE
15.5
ComparableRectangle
extends
Rectangle
and implements
Comparable
.
L
ISTING
15.10
SortRectangles.java
1
public class
SortRectangles {
2
public static void
main(String[] args) {
3
4
ComparableRectangle[] rectangles = {
create an array
new
ComparableRectangle(
3.4
,
5.4
),
5
new
ComparableRectangle(
13.24
,
55.4
),
6
new
ComparableRectangle(
7.4
,
35.4
),
7
new
ComparableRectangle(
1.4
,
25.4
)};
java.util.Arrays.sort(rectangles);
8
9
for
(Rectangle rectangle: rectangles) {
10 System.out.print(rectangle +
" "
);
11 System.out.println();
12 }
13 }
14 }
sort the array
Width: 3.4 Height: 5.4 Area: 18.36
Width: 1.4 Height: 25.4 Area: 35.559999999999995
Width: 7.4 Height: 35.4 Area: 261.96
Width: 13.24 Height: 55.4 Area: 733.496
benefits of interface
An interface provides another form of generic programming. It would be difficult to use a
generic
sort
method to sort the objects without using an interface in this example, because
multiple inheritance would be necessary to inherit
Comparable
and another class, such as
Rectangle
, at the same time.
The
Object
class contains the
equals
method, which is intended for the subclasses of the
Object
class to override in order to compare whether the contents of the objects are the same.
Suppose that the
Object
class contains the
compareTo
method, as defined in the
Comparable
interface; the
sort
method can be used to compare a list of
any
objects.
Whether a
compareTo
method should be included in the
Object
class is debatable. Since the
compareTo
method is not defined in the
Object
class, the
Comparable
interface is defined
in Java to enable objects to be compared if they are instances of the
Comparable
interface. It
is strongly recommended (though not required) that
compareTo
should be consistent with
equals
. That is, for two objects
o1
and
o2
,
o1.compareTo(o2) == 0
if and only if
o1.equals(o2)
is
true
.
✓
✓
Check
Point
15.17
True or false? If a class implements
Comparable
, the object of the class can invoke
the
compareTo
method.