Java Reference
In-Depth Information
System.out.println(
"age? "
+
student.age
);
System.out.println(
"isScienceMajor? "
+
student.isScienceMajor
);
System.out.println(
"gender? "
+
student.gender
);
}
}
The following code has a compile error, because the local variables
x
and
y
are not initialized:
class
Test {
public static void
main(String[] args) {
// x has no default value
// y has no default value
System.out.println(
"x is "
+ );
System.out.println(
"y is "
+ );
int
x;
String y;
x
y
}
}
Caution
NullPointerException
is a common runtime error. It occurs when you invoke a
method on a reference variable with a
null
value. Make sure you assign an object refer-
ence to the variable before invoking the method through the reference variable.
NullPointerException
8.5.4 Differences between Variables of Primitive Types
and Reference Types
Every variable represents a memory location that holds a value. When you declare a variable,
you are telling the compiler what type of value the variable can hold. For a variable of a prim-
itive type, the value is of the primitive type. For a variable of a reference type, the value is a
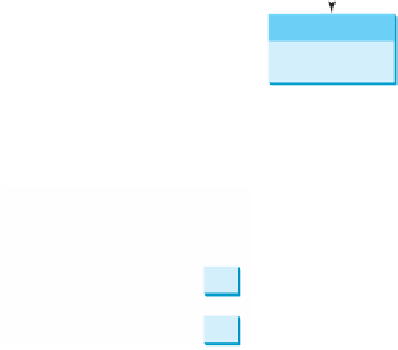
reference to where an object is located. For example, as shown in Figure 8.7, the value of
int
variable
i
is
int
value
1
, and the value of
Circle
object
c
holds a reference to where the
contents of the
Circle
object are stored in memory.
When you assign one variable to another, the other variable is set to the same value. For a
variable of a primitive type, the real value of one variable is assigned to the other variable. For
a variable of a reference type, the reference of one variable is assigned to the other variable.
As shown in Figure 8.8, the assignment statement
i = j
copies the contents of
j
into
i
for
Created using new
Circle()
int i
= 1
i
1
Primitive type
Object type
Circle c
c
reference
c: Circle
radius = 1
F
IGURE
8.7
A variable of a primitive type holds a value of the primitive type, and a variable
of a reference type holds a reference to where an object is stored in memory.
Primitive type assignment
i = j
Before:
After:
i
i
1
2
j
j
2
2
F
IGURE
8.8
Primitive variable
j
is copied to variable
i
.