Java Reference
In-Depth Information
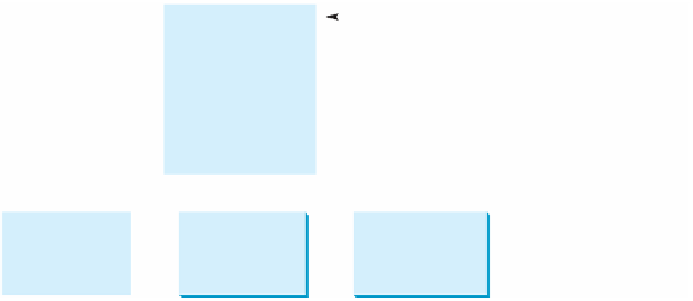
A class template
Class Name: Circle
Data Fields:
radius is _____
Methods:
getArea
getPerimeter
setRadius
Three objects of
the Circle class
Circle Object 1
Circle Object 2
Circle Object 3
Data Fields:
radius is
1
Data Fields:
radius is
25
Data Fields:
radius is
125
F
IGURE
8.2
A class is a template for creating objects.
class
Circle {
/** The radius of this circle */
double
radius =
1
;
Data field
/** Construct a circle object */
Circle() {
}
Constructors
/** Construct a circle object */
Circle(
double
newRadius) {
radius = newRadius;
}
/** Return the area of this circle */
double
getArea() {
return
radius * radius * Math.PI;
}
/** Return the perimeter of this circle */
double
getPerimeter() {
return
2
* radius * Math.PI;
Method
}
/** Set new radius for this circle */
double
setRadius(
double
newRadius) {
radius = newRadius;
}
}
F
IGURE
8.3
A class is a construct that defines objects of the same type.
The
Circle
class is different from all of the other classes you have seen thus far. It does
not have a
main
method and therefore cannot be run; it is merely a definition for circle
objects. The class that contains the
main
method will be referred to in this topic, for conve-
nience, as the
main class
.
The illustration of class templates and objects in Figure 8.2 can be standardized using
Unified
Modeling Language (UML)
notation. This notation, as shown in Figure 8.4, is called a
UML
class diagram
, or simply a
class diagram
. In the class diagram, the data field is denoted as
main class
Unified Modeling Language
(UML)
class diagram
dataFieldName: dataFieldType
The constructor is denoted as
ClassName(parameterName: parameterType)