Java Reference
In-Depth Information
The maximum of 5 and 2 is 5
line#
i
j
k
num1
num2
result
4
5
5
2
12
5
2
Invoking max
13
undefined
16
5
6
5
This program contains the
main
method and the
max
method. The
main
method is just like
any other method except that it is invoked by the JVM to start the program.
The
main
method's header is always the same. Like the one in this example, it includes the
modifiers
public
and
static
, return value type
void
, method name
main
, and a parameter
of the
String[]
type.
String[]
indicates that the parameter is an array of
String
, a sub-
ject addressed in Chapter 6.
The statements in
main
may invoke other methods that are defined in the class that con-
tains the
main
method or in other classes. In this example, the
main
method invokes
max(i,
j)
, which is defined in the same class with the
main
method.
When the
max
method is invoked (line 6), variable
i
's value
5
is passed to
num1
, and vari-
able
j
's value
2
is passed to
num2
in the
max
method. The flow of control transfers to the
max
method, and the
max
method is executed. When the
return
statement in the
max
method is
executed, the
max
method returns the control to its caller (in this case the caller is the
main
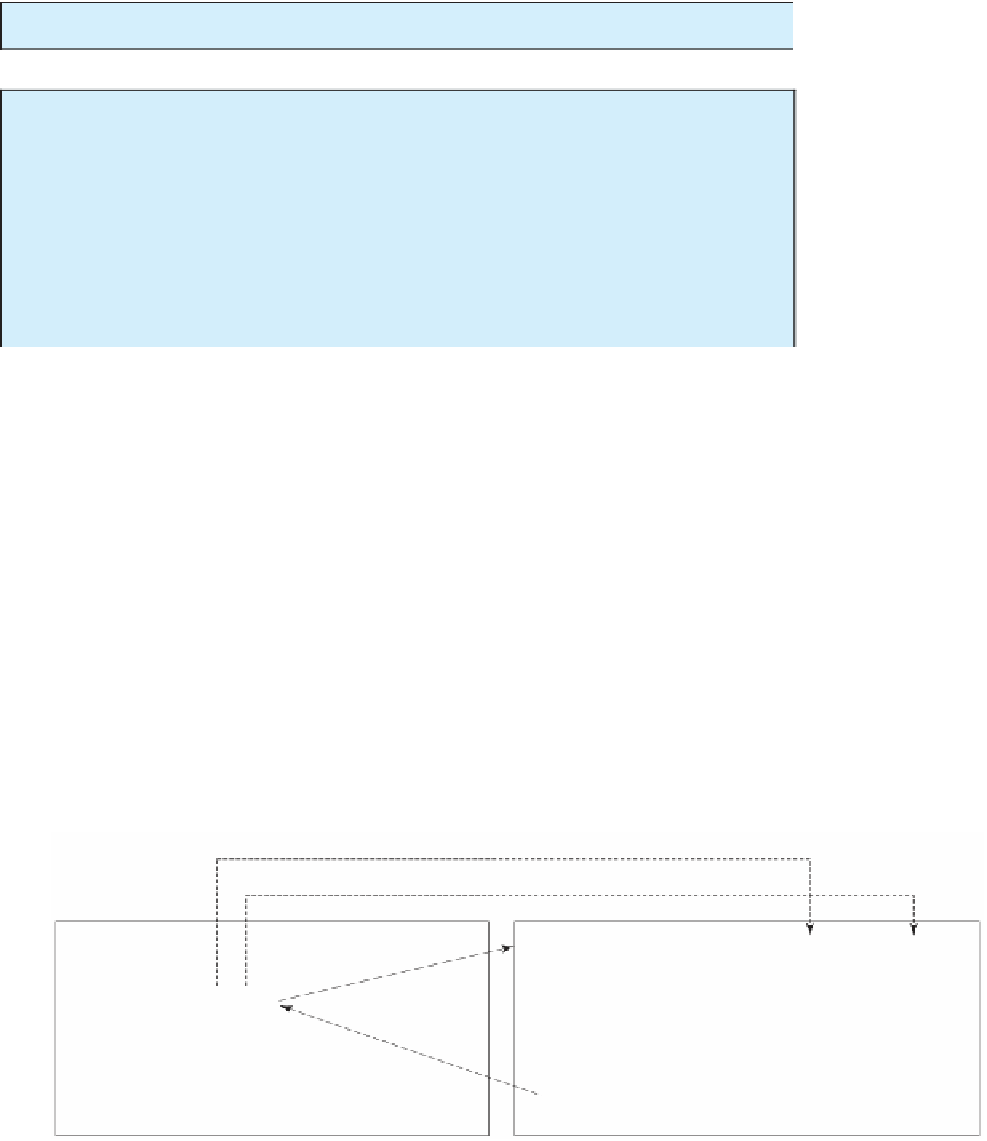
method). This process is illustrated in Figure 5.2.
main
method
max
method
pass the value
i
pass the value
j
public static void
main(String[] args) {
int
i =
5
;
int
j =
2
;
int
k = max(i, j);
public static int
max(
int
num1,
int
num2) {
int
result;
if
(num1 > num2)
result = num1;
else
result = num2;
System.out.println(
"The maximum of "
+ i +
" and " + j + " is "
+ k);
}
return
result;
}
F
IGURE
5.2
When the
max
method is invoked, the flow of control transfers to it. Once the
max
method is finished, it
returns control back to the caller.
Caution
A
return
statement is required for a value-returning method. The method shown
below in (a) is logically correct, but it has a compile error because the Java compiler
thinks that this method might not return a value.