Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
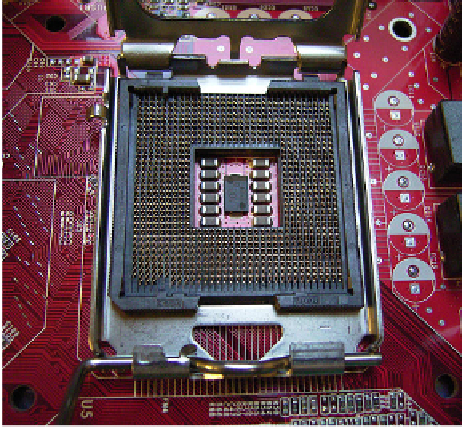
However, in recent years, this design has been replaced by land grid array (LGA), a
style that has no pins on the chip. Figure 1.2 shows an example of an LGA socket. In place
of the pins are tiny pads of bare gold-plated copper that touch corresponding pins on the
socket. The main advantage of LGA is size; the pads can be much smaller than a socketed
pin, so the CPU can contain more connection lines to the motherboard without the size of
the CPU socket becoming very large.
FIGURE 1.2
Most CPUs today use an LGA socket.
Photo credit: User Smial on de.wikipedia.
For mobile computers, where the processors and motherboards are very small, a different
type of socket is used. It's either a very small PGA socket (such as the µPGA-989) or a ball
grid array (BGA) socket, which is an updated type of PGA in which pins are replaced by
balls of solder.
Processor Speed and Performance
Just as an automobile has unique performance features that single it out from the crowd,
computer processors have specialized performance features that distinguish each model.
In this section, you'll learn about some of the ways that processor performance is measured
and enhanced.
We measure the speed of a processor in hertz (Hz), or cycles per second. Each time
the internal clock of the processor completes a full cycle, a single Hz has passed. Modern
processors operate at millions (
megahertz, MHz
) or billions (
gigahertz, GHz
) of cycles per