Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
AMD Processors
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) has been the strongest competitor to Intel in the PC
processor market since the 1990s. AMD processors have historically been less expensive
than Intel's, while offering roughly equivalent performance. Because AMD processors use a
different instruction set than Intel's, they require motherboards specially designed for them.
The
motherboard
is the large circuit board inside a PC to which everything else connects.
AMD's early CPU offerings included the K5, K6, K7, K8, and K9 processors, each
of which competed directly with an Intel processor. AMD's current lineup includes the
Phenom II, Athlon II, and Turion II lines.
Processor Sockets
Processors require the correct type of socket in the motherboard in which you're installing
them. When buying a motherboard, make sure the processor socket is appropriate for the
CPU you plan to use.
Sockets use various code names and numbering. The numbering is often based on the
number of pins, or contacts, on the chip. For example, the LGA 1356 contains 1,356 pins.
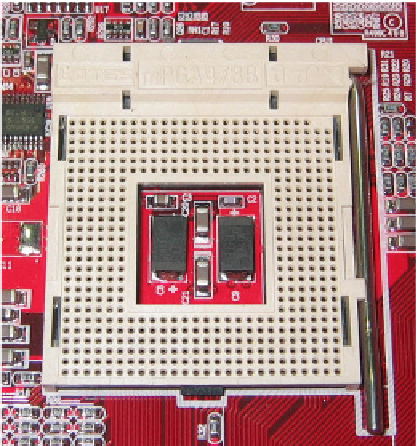
In earlier times, a pin grid array (PGA) was the preferred style of processor socket. It
consisted of a grid of tiny holes into which the tiny pins on the back of a CPU chip were
secured. Figure 1.1 shows a PGA socket in a motherboard circa 2005.
FIGURE 1.1
Pin grid array (PGA) was a common type of processor socket until a few
years ago.
Photo credit: Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
User:Berkut