Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Cache Size
Just like a processor, a hard disk has a small, integrated RAM cache for
storing data that was recently used or is probably about to be asked for. The larger the
drive's cache size, the more it can anticipate the OS's requests. Both mechanical and solid-
state drives have caches.
Types of Hard Drive Connectors
Internal hard disks connect to the motherboard via a cable that uses one of three types of
connectors:
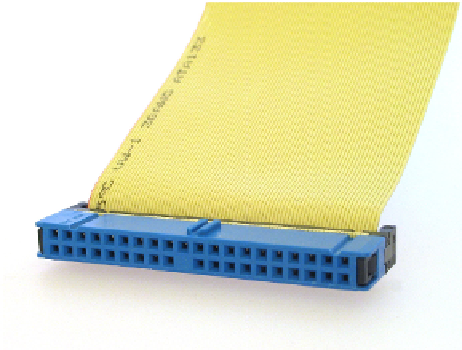
Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
An old-technology type of connector
that uses a wide ribbon-like cable with 40 wires (see Figure 2.9). Until a few years ago,
nearly all hard disks used this type of connector; now it's nearly obsolete. Multiple wires in
the cable send data bits in parallel (that is, at the same time).
FIGURE 2.9
A PATA hard disk cable
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
Like PATA, SCSI is a parallel interface; it uses a
ribbon cable that is very similar to the PATA cable shown in Figure 2.9 but slightly wider
(50 or 68 wires). SCSI was very popular in high-end systems at one point because they were
faster and you could chain many SCSI devices together on a single interface with a single
controller board. SCSI is no longer popular in mainstream systems because SATA has most
of its advantages and is cheaper.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
SATA is a newer technology connector
that uses a seven-wire plug. Data is sent serially (that is, one bit at a time). SATA drives
have the fastest data-transfer capabilities of the three, and the thinner and less bulky cables
enable better air fl ow in the case (see Figure 2.10).