Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(
A
)
(
B
)
(
C
)
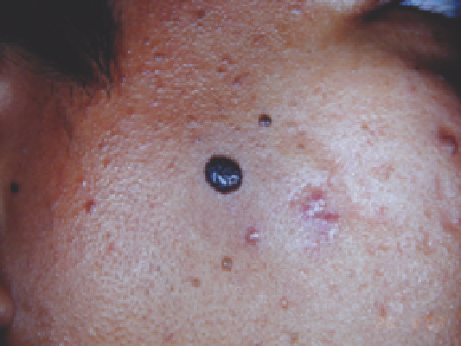
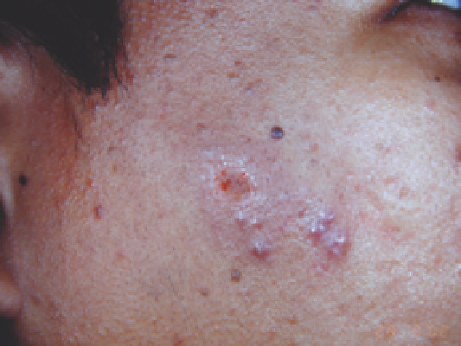
Figure 13.20
(
A
) A compound melanocytic nevus in a Thai man with skin phototype IV, before treatment. (
B
) Immediately after ablated with three passes of
continuous wave CO
2
laser with a 3-mm spot size at 3 W. (
C
) Two years after one treatment with CO
2
laser vaporization.
Abbreviation
: CO
2
, carbon dioxide.
Studies on the use of these nonablative laser devices in Asian
patients have confi rmed the effectiveness and safety of this
technique (197-199). One important concern is the occur-
rence of prolonged or permanent skin dyspigmentation that
might result from an improper parameter selection of a cryo-
gen cooling device coupled to some nonablative laser systems
or from an improper positioning of the laser handpiece, not
from the thermal injury of laser light (Fig. 13.21) (200,201).
Unfortunately, Asians with a higher epidermal melanin con-
tent are known to have an associated higher risk of PIH after
skin injury which, although transient, is associated with a sig-
nifi cant degree of patient dissatisfaction. Another more
important concern is laser-induced hypopigmentation that
can be prolonged or even permanent, particularly in pig-
mented Asian skin.
Nonablative laser skin remodeling remains a popular treat-
ment choice for patients seeking noninvasive treatment
modality and, although several systems have been shown to
effect improvement in rhytides and atrophic scars, they still do
not approximate the improvement typically seen after ablative
laser treatment. In addition, none of these light systems has yet
emerged as being clearly superior. While the absence of epi-
dermal damage in NDR techniques signifi cantly decreases the
severity and duration of the treatment-related adverse effects,
the major drawback of these techniques is their limited
effi cacy.
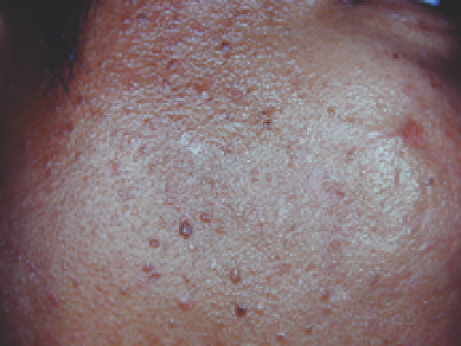
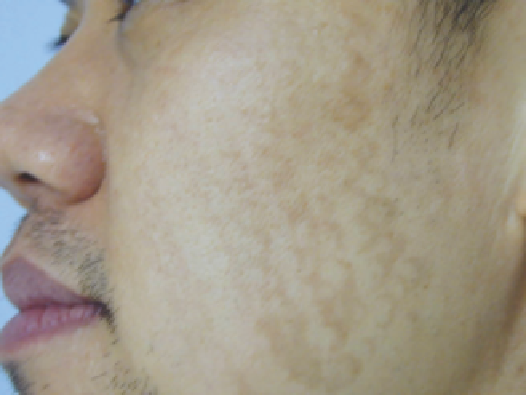
Figure 13.21
Persistence of hyperpigmented rings 3 months after a treatment
with the 1450-nm diode laser equipped with a tetrafl uoroethane spray cooling
for nonablative dermal remodeling in a 36-year-old Thai man with skin
phototype IV.
fractional resurfacing systems
The latest concept of cutaneous remodeling called FP has been
introduced in 2004 (202). Skin restoration by FP is achieved by
applying an array of microscopic treatment zones (MTZs) of
thermal injury to the skin. The concept behind this approach