Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
niveiconis
Eastern Africa to Cameroun
I
I
nero
Cameroun
telisignata 2-4, 17, 18
similis 16
obscurior 16, 17
I
l
cynthia 25-27
/eggei 22, 25-27
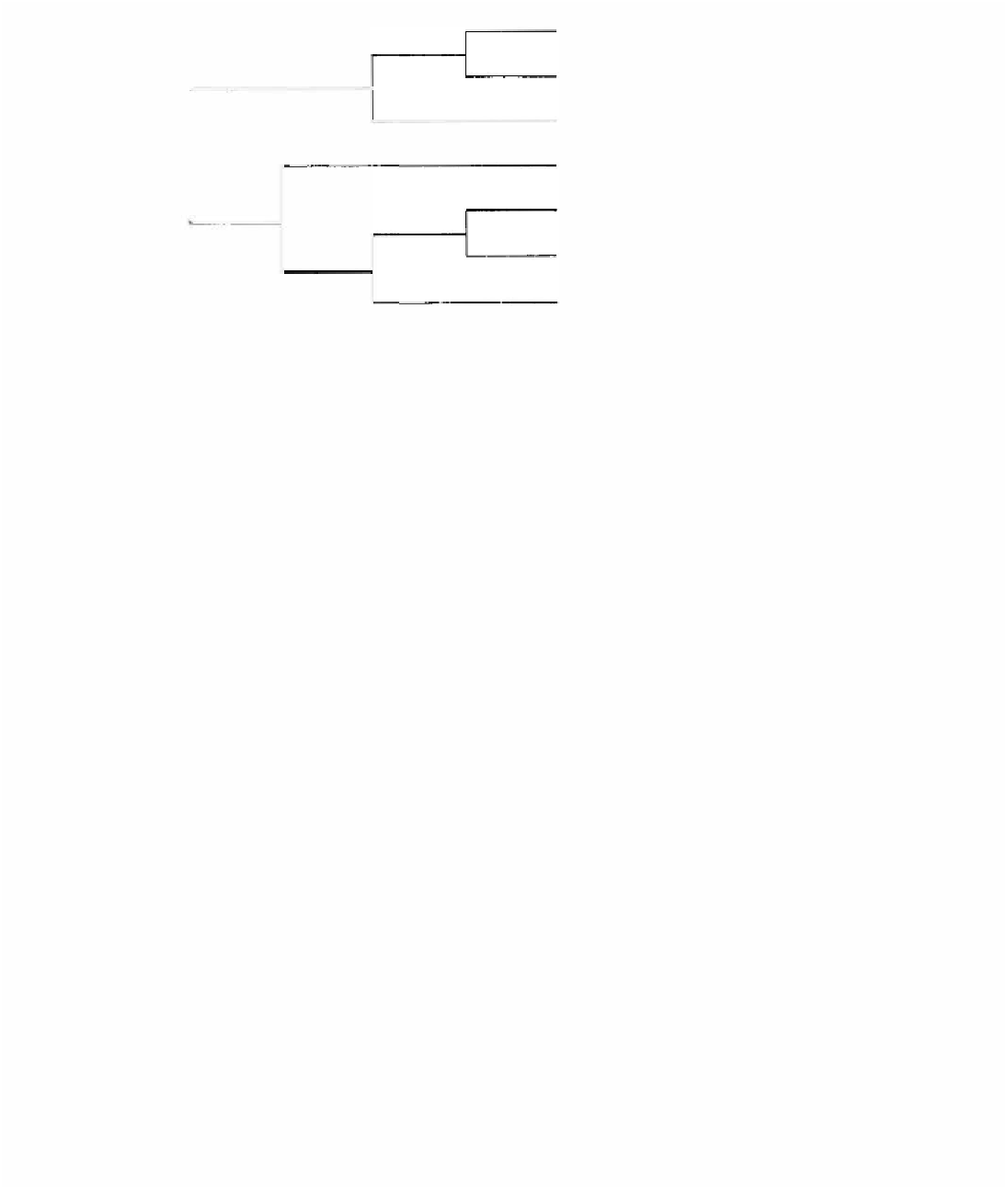
Figure 8.2. Phylogeny and distribuion of the genus
Chondrolepis,
after de Jong (1986).
Names in bold refer to Afromontane forest species. Numbers refer to the areas listed in
Table 8.1.
/eucotaenia group, /eucotaenia; sole species of the
group; sister group of the dela/andei
(Madagascar), phorcas (throughout Africa)
and
hespeus
groups combined;
hespeus
group,
nobi/is, pelodorus;
three more
species in the group, in forests, one of
which also in the study area at lower
elevaions;
nireus group, mackinnoni to thuraui; nine more
species in the group; ch aropus also in
Cameroun (nominotypical subspecies); the
group was studied by Hancock (1984); for
the phylogenetic relationships and
distributions, see Figure 8.3;
rex group, rex; sole species of the group, also
represented in Cameroun by a separated
subspecies; sister group of the ynorta
group;
ynorta group, echerioides through sj oestedti; three
more species in the group, in forests at
lower elevaions, two also in the study area.
P. echeioies extends southward in two
subspecies to Zimbabwe and
Natal/Transvaal.
All species are found in woodland and open
habitats, often quite arid. . elgonensis is the only
species of the genus found in (and restricted to)
highland forest, not only in EAT but also in
Cameroun. In the study area 30 more species
occur.
Belenois (Pieridae). lndo-African, with 23 species
in the Afrotropical region, one of which occurs in
India as well. The species are found in open
habitats, woodland and forest. In addition to the
species in Appendix 8.2, 11 more species occur in
the study area.
My loth ris (Pieridae). An African genus of 31
woodland and forest species. In addiion to the
species in Appendix 8.2, 12 more species occur in
the study area. Carcasson (1981) treats leonoa as
subspecies of M. crawshayi; this is followed here.
M. saga/a extends south to east Zimbabwe (separ-
ate subspecies), and also occurs in Cameroun
(also separate subspecies).
Alaena (Lycaenidae). The genus is strictly
Afrotropical and belongs to an endemic African
subfamily, Lipteninae. It numbers 22 species in a
wide range of habitats from arid open condiions
to forest. It does not occur in West Africa. In
addiion to the four species in Appendix 8.2, 10
more species occur in the study area.
Colotis
(Pieridae). A mainly African genus with 42
species in the Afrotropical region, one of which
also occurs in North Africa and occasionally in
southern Spain. Three other African species
extend into India where four more species occur.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search