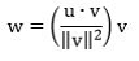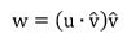Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
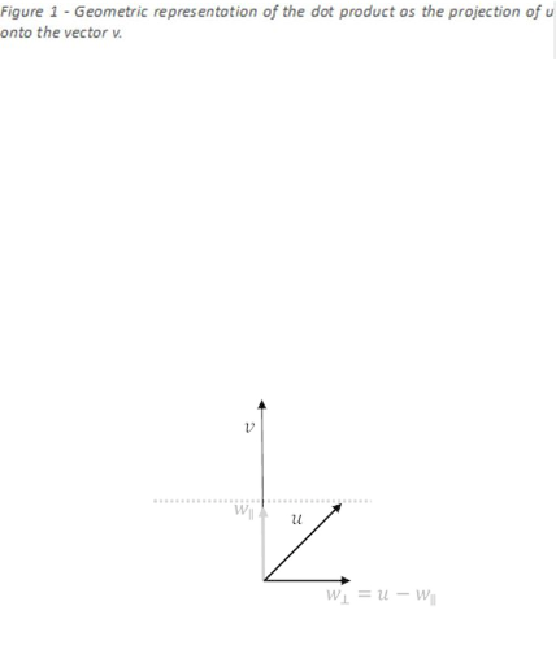
The projection of an arbitrary vector
u
onto a vector
v
is defined by:
If
v
is a normalized vector
û
, then the projection can be simplified to
A useful thing to note is that this will be the part of
u
that is parallel to
v
, we can use this
facttocomputethepartof
b
thatisperpendicular to
v
bysubtracting theprojection from
u.
Figure 7 - Using the dot product to compute a perpendicular vector.
This fact is useful when calculating the distance from a point to a line. Given a point
p
and
a line defined by two points
p0,p1
we can define two vectors,