Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
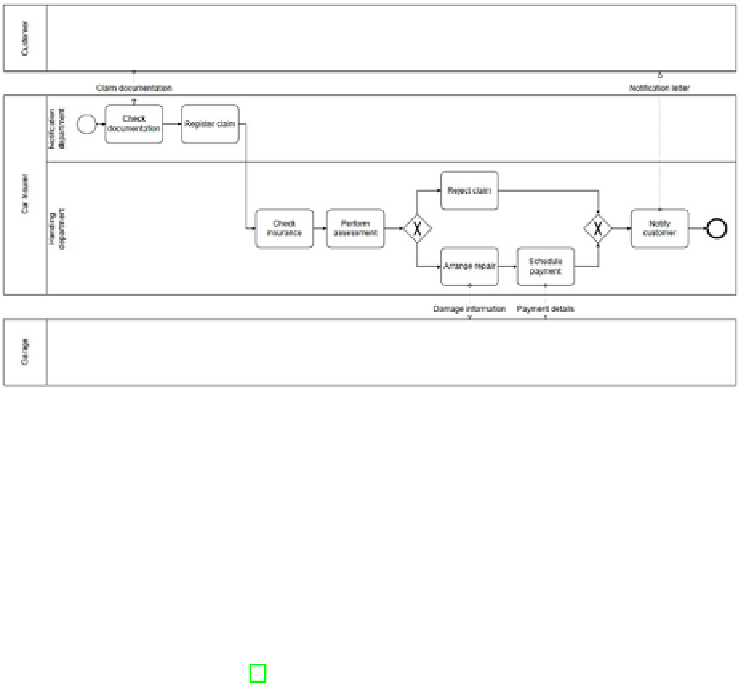
Fig. 1.
Example of a claims handling process in BPMN
the documents upon completeness and registers the claim. Then, the Handling
department picks up the claim and checks the insurance. Then, an assessment
is performed. If the assessment is positive, a garage is phoned to authorise the
repairs and the payment is scheduled (in this order). Otherwise, the claim is re-
jected. In any case (whether the outcome is positive or negative), a letter is sent
to the customer and the process is considered to be complete.” Such information
is usually provided by people working in the process and then formalized as a
model by system analysts [2].
For our model generation approach, we will employ methods from compu-
tational linguistics and natural language processing. This branch of artificial
intelligence deals with analyzing and extracting useful information from natural
language texts or speech. For our approach, three concepts are of vital impor-
tance: syntax parsing, which is the determination of a syntax tree and the gram-
matical relations between the parts of the sentence; semantic analysis, which
is the extraction of the meaning of words or phrases; and anaphora resolution,
which involves the identification of the concepts which are references using pro-
nouns (“we”,“he”,“it”) and certain articles (“this”, “that”). For syntax parsing
and semantic analysis, there are standard tools available.
The Stanford Parser is a syntax parsing tool for determining a syntax tree.
This tree shows the dependencies between the words of the sentence through the
tree structure [10]. Additionally, each word and phrase is labeled with an appro-
priate part-of-speech and phrase tag. The tags of the
Stanford Parser
are the
same which can be found in the
Penn Tree Bank
[11]. The
Stanford Parser
also
produces 55 different
Stanford Dependencies
[12]. These dependencies reflect the
grammatical relationships between the words. Such grammatical relations pro-
vide an abstraction layer to the pure syntax tree. They also contain information
about the syntactic role of all elements.