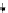Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Creation of
master record
for tangible
assets
Creation of
leased asset
master record
Creation of
group asset
XOR
XOR
Asset master
record is
incomplete
Asset master
record is
incomplete
Fixed asset
created
Leased asset
is created
V
XOR
XOR
Depreciation
should be
posted
regularly
V
Depreciation
should be
posted
regularly
V
Retirements to
be entered
Retirements to
be entered
Depreciation
terms should
be changed
Cost center
plan was
changed
Several asset
master records
should be
changed
Depreciation
terms should
be changed
Cost center
plan was
changed
Post-
capitalisation
to be posted
Post-
capitalisation
to be posted
Several asset
master records
should be
changed
Fig. 7.
Excerpts of two process variants in the SAP reference model
larger than the threshold. For these clusters, Table 1 depicts the number of
clusters, their average and maximal size, and the number of considered models.
For instance, requiring variants to share at least 12 nodes led to 23 clusters
comprising 56 distinct models. The average size of the clusters is three models,
the maximum size is seven models. The derived values witness the existence of
a large number of process variants in the model collection.
In order to analyse the commonalities for all identified model clusters, we
implemented the presented set algebra and derived the LCM. This analysis re-
vealed that the behavioural profile of the LCM was often equal to the profile
of at least one model in the cluster. Based on this observation, we checked for
all clusters of variants whether the behavioural profile of one variant includes
the profiles of all other variants for the shared nodes. In fact, this was the case
for all but two clusters. The identified LCM models could be used as a starting
point for harmonising the reference model by removing redundant variants and
integrating their non-shared nodes into the former model. Consider, for instance,
the excerpts of two encountered process variants in Fig. 7. Both models share 16
nodes, some of them are highlighted in the excerpt. For some shared nodes both
models define different behavioural constraints. Still, the behaviour of the right
model includes the behaviour of the left model for shared nodes, which suggests
integration of the processing defined by the left model into the right one.
Using this approach, more than half of the identified variants could be removed
from the collection as indicated by the last row in Table 1. Depending on the
number of required shared nodes, the reference model could be reduced by up
to 127 process models.
6 Related Work
Research related to our work is conducted mainly in three areas: comparison of
behaviour, modelling of process variants, and behaviour synthesis.
The comparison of behaviour as defined by the operators in this paper is re-
lated to various notions of behavioural equivalence of the linear time - branching