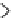Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Is Part Of
Ensure traffic
safety in its
sector
Team Sector
R
Ensure safe
operations of a
team
Supervise
Supervisor
AND
AND
Play
Manage traffic in
sector
Manage ibound
traffic
Form team
sectors
Alice
++ D
++ D
Is Part Of
Te
Manage traffic in
sector SU1
Te
Play
Play
Executive
Controller
Planning
Controller
Bob
Play
Manage traffic in
sector
P
-
Dan
Manage inbound
traffic
-
Resolve traffic
conflict
Overload Traffic
Fig. 1.
A SI* Diagram from a fragment of the Air Traffic Management scenario
A SI* model captures relationships between concepts using several basic relations:
1)
AND/OR-decomposition
to refine a goal, 2)
contribution
to capture the effects of
a goal to another, 3)
impact
to model the impact of an uncertain event to a business
object. Fig. 1 depicts the goal
ensure traffic safety in its sector
is AND-decomposed
into
manage traffic in sector
and
manage inbound traffic
, where the achievement
of both subgoals are necessary to achieve the up-level goal. Moreover, the achievement
of the latter goal contributes positively to the success of the former one. In ATM, we
consider the effect of
overload traffic
event to the goal
manage traffic in sector
,and
it can be mitigated with the capability of an actor in
resolve traffic conflict
.
4
Formalizing Patterns
Our formalization process includes four steps: (i) Formalize the SI* language by defin-
ing non-overlapping OWL-
concepts for all SI* primitives and one or more roles
for every primitive SI* relationship; (ii) Formalize the context of each pattern using
the concepts and roles introduced in step (i); (iii) Enrich the formal pattern descrip-
tions with implicit knowledge
1
; (iv) Represent the problem-at-hand in the ABox by
instantiating the concepts and roles of step (i).
DL
4.1
Formalizing SI* Primitives
In general, we represent nodes (e.g., goal, task, resource, event) in a SI* model as con-
cepts and binary relations (e.g., actor's associations, contributions, decompositions, im-
1
Availability of a domain expert is essential here because this implicit knowledge (constraints,
alternatives, and more) is often missing from the informal pattern description.