Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Contribution:
The goal of the presented paper is to show, how the deficiencies of the
models resulting from the text can be used to generate feedback for human analysts.
The feedback can be presented in two forms: (1) in natural language and (2) by spe-
cial markings on the produced models. The effectiveness of the generated feedback
was evaluated in an experiment and it was found that the generated feedback can ad-
dress genuine problems of requirements specifications that would be overseen by human
analysts.
Outline:
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents our
approaches to text-to-model translation, used as the basis for the presented work on
feedback generation. Sections 3 and 4 are the technical core of the paper, they present
the feedback generation and its evaluation. Finally, Section 5 gives an overview of
related work and Section 6 summarizes the paper.
2
From Text to Models: Our Existing Approaches
In our survey of existing modeling techniques [2] it was shown that all existing in-
dustrially relevant formalisms are based either on interaction sequences or on finite
automata. For this reason, the target model types for the behavior modeling are either
finite automata or Message Sequence Charts (MSCs), serving as a representative for
interaction-based modeling techniques. The translation from text to MSCs is presented
in Section 2.1, and the translation to finite automata in Section 2.2.
2.1
From Scenarios to Message Sequence Charts
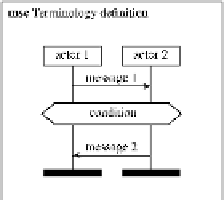
Translation of textual scenarios to message sequence charts was presented in [3,4]. For
the translation we assume that every message sequence chart (MSC) consists of a set
of
actors
, a sequence of
messages
sent and received by these actors, and a sequence of
conditions
(or
assertions
) interleaved with the message sequence. This terminology is
illustrated in Figure 1.
Fig. 1.
MSCs, terminology
The basic idea of the scenario-to-MSC translation can be illustrated on the following
scenario, taken from the Instrument Cluster Specification [5]: