Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Architecture of replica sets
After learning the replication process, we can go ahead and learn about the replica set ar-
chitecture. In order to create a readily available MongoDB server, you can simply use the
replica set network.
So, what is replica set?
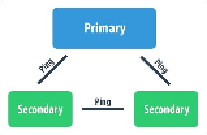
Each replica set consists of different members and each one is responsible for a particular
task. The following list shows you all the possible roles for each member:
•
Primary
: A
primary
node is responsible for accepting all read/write operations
from clients. Each replica set can have one and only one
primary
node. Under
some conditions, a
primary
node can become
secondary
or a
secondary
node can become
primary
by an election process.
•
Secondary
: The
secondary
nodes host the same dataset as
primary
nodes.
Each replica set can have one or more
secondary
nodes. It's possible that a
secondary
node changes its state and becomes a
primary
node by the election
process.
•
Arbiter
: An
arbiter
node is used to facilitate the election procedure. An
ar-
biter
node won't change its state. The
arbiter
node doesn't host any dataset
and only votes in the election process. On the other hand, the
arbiter
node
doesn't need any dedicated hardware.
The following screenshot illustrates the architecture of
primary
,
secondary
, and
ar-
biter
nodes: