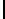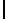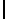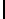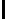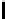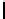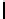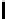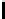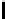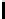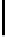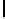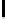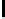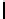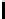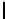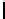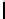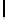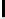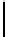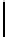Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 1 .
Accuracies of the significance classifier for different fixed distributions (0
∗
indicates p
values
<
0
.
001)
μ
1
=
20
,
sd
1
=
2
,
μ
2
=
21
,
sd
2
=
2
Appr. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95
Sign.Cl.
.
655
.
698
.
751
.
770
.
810
.
825
.
836
.
855
.
865
.
895
.
898
.
909
.
915
.
928
.
929
.
935
.
944
.
940
.
952
p
thresh.
.
570
.
628
.
660
.
716
.
763
.
783
.
810
.
839
.
857
.
887
.
891
.
903
.
922
.
930
.
933
.
940
.
947
.
946
.
955
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
.
001
.
004
.
151
.
171
.
129
.
185
.
845
.
636
.
783
.
914
.
688
.
908
.
755
p
(t-test)
μ
1
=
20
,
sd
1
=
2
,
μ
2
=
22
,
sd
2
=
2
Appr. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95
Sign.Cl.
.
784
.
865
.
910
.
942
.
957
.
972
.
975
.
984
.
989
.
991
.
989
.
995
.
996
.
996
.
998
.
999
.
998
.
998
.
997
p
thresh.
.
708
.
836
.
911
.
947
.
960
.
970
.
974
.
976
.
974
.
974
.
976
.
975
.
974
.
976
.
973
.
980
.
973
.
976
.
975
(t-test)
0
∗
0
∗
.
561
.
825
.
807
.
341
.
408
.
0210
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
p
μ
1
=
20
,
sd
1
=
2
,
μ
2
=
23
,
sd
2
=
2
Appr. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95
Sign.Cl.
.
893
.
958
.
972
.
986
.
994
.
997
.
997
.
997
.
997
.
999
.
999
.
999 1
.
0 1
.
0 1
.
0 1
.
0 1
.
0 1
.
0 1
.
0
p
thresh.
.
865
.
959
.
970
.
970
.
97
.
975
.
977
.
976
.
973
.
974
.
980
.
975
.
975
.
976
.
975
.
972
.
974
.
976
.
974
(t-test)
0
∗
.
653
.
418
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
p
Ta b l e 2 .
Accuracies of the significance classifier for randomly generated distributions (0
∗
indi-
cates p values
<
0
.
001)
Appr. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95
Sign.Cl.
.
563
.
601
.
655
.
680
.
701
.
717
.
733
.
730
.
745
.
761
.
775
.
780
.
778
.
777
.
793
.
808
.
801
.
790
.
806
p
thresh.
.
539
.
564
.
580
.
599
.
612
.
615
.
626
.
627
.
635
.
634
.
646
.
642
.
649
.
652
.
653
.
666
.
654
.
654
.
658
.
014
.
0020
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
0
∗
p
(t-test)
-
Generate random mean value for the second distribution within the standard devia-
tion of the first one:
μ
2
∈
sd
1
,μ
1
+
sd
1
]
.
-
Randomly select a standard deviation value for the second distribution:
sd
2
∈
[0
,
2
sd
1
]
[
μ
1
−
Instead of drawing random samples from the same distribution, in this experiment series
for each training and testing example, the distributions are generated randomly. Thus,
more general classifiers are trained taking into account various different distributions.
Once again, ten independent runs with 500 training and 500 testing examples are per-
formed. The results (average accuracies and p value of t-tests) of these experiments are
presented in Table 2. A graph comparing the significance classifier with the p-threshold
method is shown in Figure 6. The results indicate better results of the classifier for all
tested numbers of p values. In some cases an accuracy difference with approximately
15 percent points occurs in these experiments.
5.3
Replication Prediction for Fixed Distributions
The third part of the evaluation addresses the replication prediction. Additionally to
the approach presented in Section 4.3, we use a statistical power analysis in order to