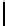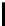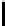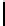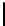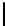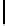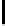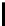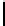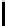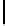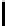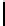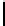Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 1 .
Evaluating norm 1
Ta b l e 2 .
Evaluating norm 3
Norm
Contribution
positive neutral negative
Norm
Contribution
positive neutral negative
Obligation
1
0
0
Prohibition
0
0
1
Reward
1
0
0
Reward
1
0
0
Reward
1
0
0
Reward
1
0
0
Punishments
Obligation
Punishments
Obligation
0
0
1
0
0
1
Ta b l e 3 .
Evaluating norm 2
Norm
Contribution
positive neutral negative
Prohibition
0
0
1
Punishments
Obligation
0
0
1
Obligation
0
0
1
greater than the contribution for violating it that is equal to “-1”. It indicates that the
agent has the intention to fulfil the three norms.
Detecting and Solving Conflicts (DSC).
If two different norms (one being an obliga-
tion and the other one a prohibition) specify the same state, it is important to check their
status, i.e., to check if they are in the set of norms that will be violated or fulfilled since
they may be in conflict. If the agent intends to fulfil the obligation but does not intend to
fulfil the prohibition, these norms are not in conflict. The same can be said if the agent
intends to fulfil the prohibition and to violate the obligation. On the other hand, if the
agent intends to fulfil both norms or to violate both norms, they are in conflict and it
must be solved. Such step is represented in
Algorithm
6.
For instance, in case of conflicts between two norms that the agent intends to fulfil
or violate, the one with highest contribution to the achievement of the agent's desires
(and intentions) can be selected. If the contributions have equal values we can choose
anyone. That is, if the contribution coming from the fulfilment of the first norm (Steps
1, 2 and 3) plus the contribution coming from the violation of the second norm (Steps
4.1 and 4.2) is greater to or equal than the contribution coming from the fulfilment of
the second norm plus the contribution coming from the violation of the first norm, the
first norm is selected to be fulfilled and the second one to be violated. It is represented in
Algorithm
7 from line 5 to 8. In case the opposite happens, the second norm is selected
to be fulfilled and the first to be violated, as described in
Algorithm
7 from line 8 to 11.
Considering the norms evaluated in the
EN
function, a conflict between Norm 1 and
2 is detected and should be solved. The conflict is solved by selecting Norm 1 to be
fulfilled and Norm 2 to be violated since the contribution coming from the fulfilment of
the first norm (+3) plus the contribution coming from the violation of the second norm