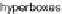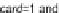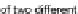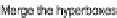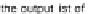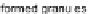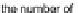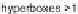Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
2
Data Granulation
The method of granulation is based on maximization of information density from point-
type data. There are hyperboxes created, which cover areas densely populated by data
objects. The hyperboxes (referred as
I
) are multi-dimensional structures described by
apairofvalues
a
and
b
for every dimension. The point
a
i
and
b
i
represent minimal
and maximal value of the granule in
i
-th dimension respectively, thus, width of
i
-th
dimensional edge equals
|
b
i
−
a
i
|
.
Fig. 1.
Algorithm of hyperboxes construction
The main steps of the algorithm are presented in Figure 1. Information density can
be expressed by Equation 1:
card
(
I
)
φ
(
width
(
I
))
,
σ
=
(1)
where
card
(
I
)
denotes the number of data points belonging to hyperbox
I
and
φ
(
width
(
I
))
is a function of hyperboxes width described by Equation 2. Belonging to a hyper-
box means, that the values of point attributes are between or equal the minimal and
maximal values of the hyperbox attributes. For that reason there is a necessity to re-
calculate cardinality in every case of forming a new larger granule from a combination
of two granules. Maximization of
σ
is a problem of balancing the possible shortest
dimensions against the greatest cardinality of formed granule
I
.
In case of multi-dimensional granules as a function of hyperboxes width the function
from Equation 2 is applied:
φ
(
u
)=exp(
K
·
max
i
(
u
i
)
−
min
j
(
u
j
))
,i,j
=1
,...,k
(2)
where
k
represents a number of dimensions,
u
=(
u
1
,u
2
,...,u
k
)
and
u
i
=
width
([
a
i
,
b
i
])
for
i,j
=1
,...,k
. The points
a
i
and
b
i
denote minimal and maximal value in
i
-th
dimension respectively. Constant
K
originally equals 2, however, in the experiments
different values of a given as parameter
K
have been used used.