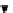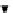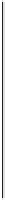Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Check bearing stress
1066.0
52
(
1.00
)(
1.00
)
=
σ
bc
=
20.5
≤
f
B
ksi
l
e
F
u
2
d
b
=
(
1.5
)(
65
)
2
(
7
/
8
)
f
B
=
=
55.7 ksi
assuming a minimum loaded edge distance of 1.5 in., OK
or
f
B
=
1.2
F
u
=
1.2
(
65
)
=
78 ksi
Since the weaker tension flange splice will govern at ultimate conditions,
a stronger compression flange splice is not required. Therefore, both top
and bottom flange splices will consist of 52 bolts each side of the double
shear splice, provided the splice is strong enough to transmit the actual
compression flange force of 1031.5 kips.
1031.5
(
2
)(
17.0
)(
0.6
)
=
n
fs
=
51
≤
52 provided, OK
Longjoints,particularlyafterslippage,donotprovideforanequaldistribu-
tion of bolt shear stress at gross section yielding. Therefore, the average bolt
shear strength will be decreased in longer joints and, effectively, the joint has
a lower factor of safety against yielding than bolts in shorter joints. However,
theoretical and experimental investigations have shown that for joints less
than about 50 in long, the FS remains at least 2.0, which is acceptable (Kulak
et al., 1987). For long joints it is often recommended to consider reducing the
allowable bolt shear stress by 20% to ensure FS
≥
2.0.
Web plate splices
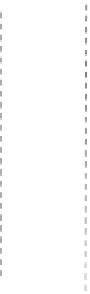
Try a web splice using 1/2 in. plates with 42 bolts each side of the splice in
the 85 in web plate shown in Figure E9.12.
2-1/2"
6"
6",typ.
6'-9"
85"
1-5/8"
2@4"
FIGURE E9.12