Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
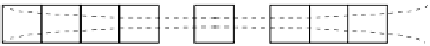
(a)
δ
(b)
l
(c)
Intermediate elastic
support, C, typical
FIGURE 5.30
End restraint with intermediate transverse elastic frames: (a) pinned ends; (b)
unrestrained ends; (c) elastic ends.
Assuming that the compression chord or flange is rigidly connected
∗
at the ends
and elastically supported at equally spaced transverse frames (girder/knee brace and
floorbeam/deck),
†
the force (reaction),
R
F
, at the transverse frames is
R
F
=
C
δ
.
(5.42)
Furthermore, assuming that the span buckles in a half-wave with continuously dis-
tributed elastic intermediate supports between ends of the span (Figure 5.30a),
Engesserprovidedthesolutionfortherequiredspringconstant,
C
req
,as(Bleich,1952)
F
cr
l
2
F
cr
4
k
2
l
,
4
EI
=
π
C
req
=
(5.43)
where
F
cr
is the compression chord or flange critical buckling force (for entire
chord/flange supported by transverse elastic frames or for length between the
transverse frames with elastic end supports) and
kl
is the effective panel length.
However, because Equation 5.43 is only accurate when the half-length of the
buckled chord or flange is greater than about 1.8
l
, it is not applicable to short-span
bridges or spans with only a few panel points. A considerably larger spring constant
(
2
F
cr
/k
2
l)
is required if it is assumed that the ends of the girder or pony truss
are laterally unsupported (
Figure 5.30b)
(Davison and Owens, 2003). This condition
is unlikely and an analysis performed by Holt (1952, 1956) that provides for end
supports modeled as cantilever springs is applicable to short spans (Figure 5.30c).
The results of this analysis and associated design procedure are given in Galambos
(1988). In such analyses, the compression area for through plate girders is generally
taken as the area of the top flange and 1/3 of the web compression area.
π
∗
The assumption of pin-connected span ends will result in a nonconservative analysis for short spans.
†
Also assuming that the chord or flange has a constant cross-sectional area and moment of inertia.