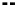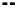Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
5.2.1.3.1 Maximum Shear Force in Simply Supported Spans [with
Concentrated Moving Loads Applied Directly to the
Superstructure
(
Figure 5.18)
]
Equating maximum shear force,
V
C
, from Equation 5.1 with the shear force,
V
Ce
,at
location C from an equivalent uniform load,
w
ev
, yields
−
P
L
2
L
(L
.
P
T
x
T
L
w
ev
=
(5.23)
−
a)
2
Equation 5.23 can be plotted for different
P
T
and
P
L
(which are dependent on load
configuration and span length) at locations C on the span.
Figure 5.19
shows the
equivalent uniform load for shear force at the end, the 1/4 point and the center of the
span for a Cooper's E80 series of concentrated moving wheel loads applied directly
to the superstructure.
5.2.1.3.2 Maximum Shear Force in Simply Supported Spans [with
Concentrated Moving Loads Applied to the Superstructure
by Transverse Members
(Figure 5.20)]
The location in the panel BC where the shear due to an equivalent uniform load,
V
BCe
=
0, is
(L
−
a)s
p
L
−
(L
a)
=
=
d
1
,
(5.24)
−
s
p
n
p
−
where
n
p
=
L/s
p
is the number of equal length panels.
P
T
P
L
P
n
C
A
B
b
n
x
T
a
L
/2
L
/2
w
e
V
Ce
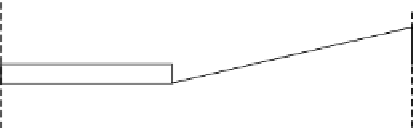
FIGURE 5.18
Equivalent uniform load for shear force for concentrated moving loads applied
directly to the superstructure.