Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
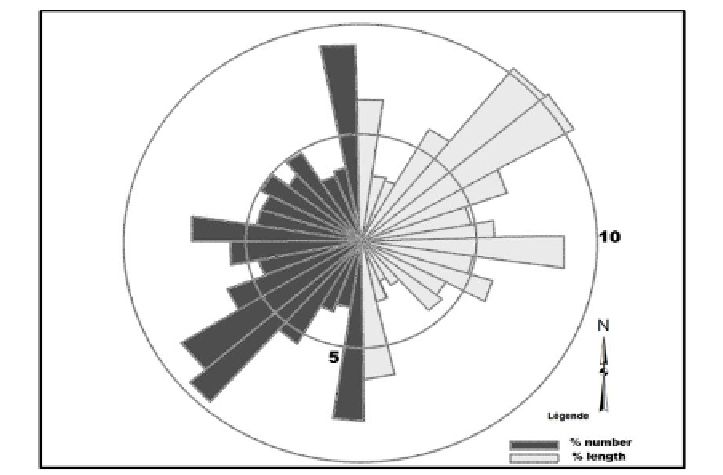
Figure 5. Rose diagramm of lineament orientations.
II.5. Drainage Network
Drainage network is a factor which depends essentially on watershed
physiography including: its shape, size, slopes, geological formations etc. Like
slope, the drainage network is inversely proportional to groundwater storage.
An important drainage network means, a higher runoff that reduces
groundwater storage capacity. In the study area, impermeable nature of the
hard rock formations explains a very high density of the drainage network,
which essentially corresponds to intermittent streams that dry up earlier as of
January. However, if the topographical conditions are favorable (low slope)
these gullies which accompany the riverbeds, can constitute substantial
groundwater reserves with low lateral extension at the scale of villages.
NDVI =
=
(Eq. 1)
Nearly all satellite Vegetation indices employ this difference to quantify
the density of plant growth on the Earth: near infrared minus visible radiation
divided by near-infrared radiation plus visible radiation.