Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
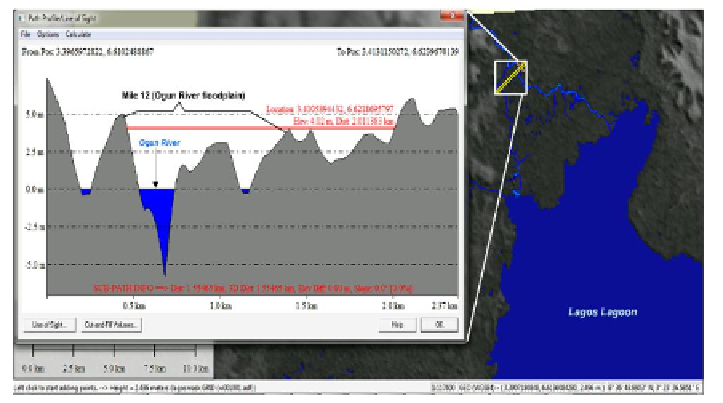
Figure 8. Cross profile of Mile 12 in the Ogun River floodplain showing the possible
maximum inundate-distance when the river rises up to 4 meters above its normal level.
4.4. Extracting Potential Flood Risk Mask
Identification of areas having higher flood hazard potential is the most
effective measure to mitigate the impact of the hazard and the first step to
formulation of sustainable flood management strategy. The issue of creating a
reliable flood hazard map (that show areas with high degree of susceptibility)
is one of the foremost concern within the field of flood disaster management
(Sanyal and Lu, 2004).
To map out the areas having high probability to be flooded, this chapter
suggests that the likelihood for a hinterland to be flooded (as a result of rain
induced excess runoff, waves etc.) is directly linked to the proximity of the
hinterland to agent of flood (hydrographic features) and the closeness of such
hinterland's elevation to the source water level. From the multi-ring buffered
hydrographic data and the CDTM created in previous sections, a flood risk
mask was generated through series of spatial analysis techniques-overlay
intersect, spatial join, union and erase functions.
The categorization of the potential flood risk areas by magnitude was done
based on the CDTM and proximity data (Table 2). This is because as noted by
Nkeki et al., 2013, the devastating impact of flooding disaster decreases with
increasing distance from the source river channel.