Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
found within an image—red, green and blue—and sends it down a single wire to the display
device, typically an old cathode-ray tube (CRT) TV.
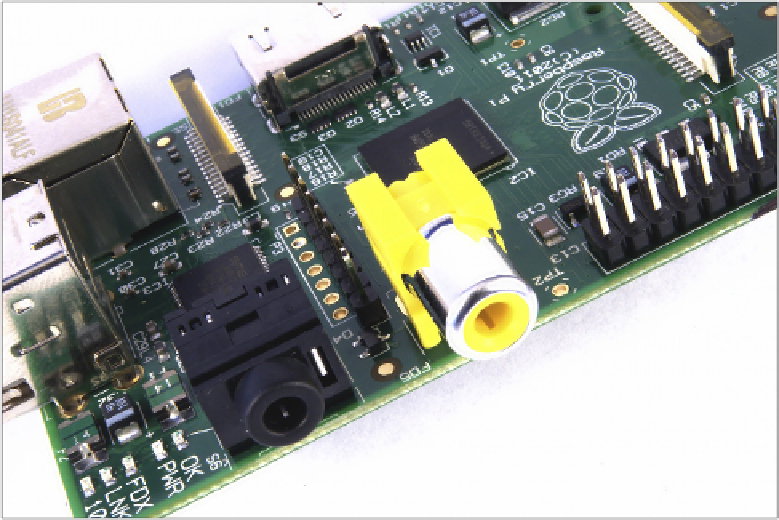
Figure 1-2:
he yellow
RCA phono
connector, for
composite video
output
When no other display device is available, a composite video connection will get you started
with the Pi. he quality, however, isn't great. Composite video connections are signiicantly
more prone to interference, lack clarity and run at a limited
resolution,
meaning that you can
it fewer icons and lines of text on the screen at once.
HDMI Video
A better-quality picture can be obtained using the
HDMI (High Deinition Multimedia Interface)
connector, the only port found on the bottom of the Pi (see Figure 1-3). Unlike the analogue
composite connection, the HDMI port provides a high-speed digital connection for pixel-
perfect pictures on both computer monitors and high-deinition TV sets. Using the HDMI
port, a Pi can display images at the Full HD 1920x1080 resolution of most modern HDTV
sets. At this resolution, signiicantly more detail is available on the screen.
If you're hoping to use the Pi with an existing computer monitor, you may ind that your dis-
play doesn't have an HDMI input. hat's not a disaster: the digital signals present on the HDMI
cable map to a common computer monitor standard called
DVI (Digital Video Interconnect
). By
purchasing an HDMI-to-DVI cable, you'll be able to connect the Pi's HDMI port to a monitor
with DVI-D connectivity.