Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
the height of cars, and it gradually decreases with the increase of
iterative times.
The classification accuracy relies heavily on the quality of
segmentation. The abundant spectral information from color
aerial image is beneficial to the classification. On the other hand, it
increases the difficulty in segmentation due to spectral confusion
between-class and spectral variation within-class. For example,
the roof material of a building along a road sometimes is similar
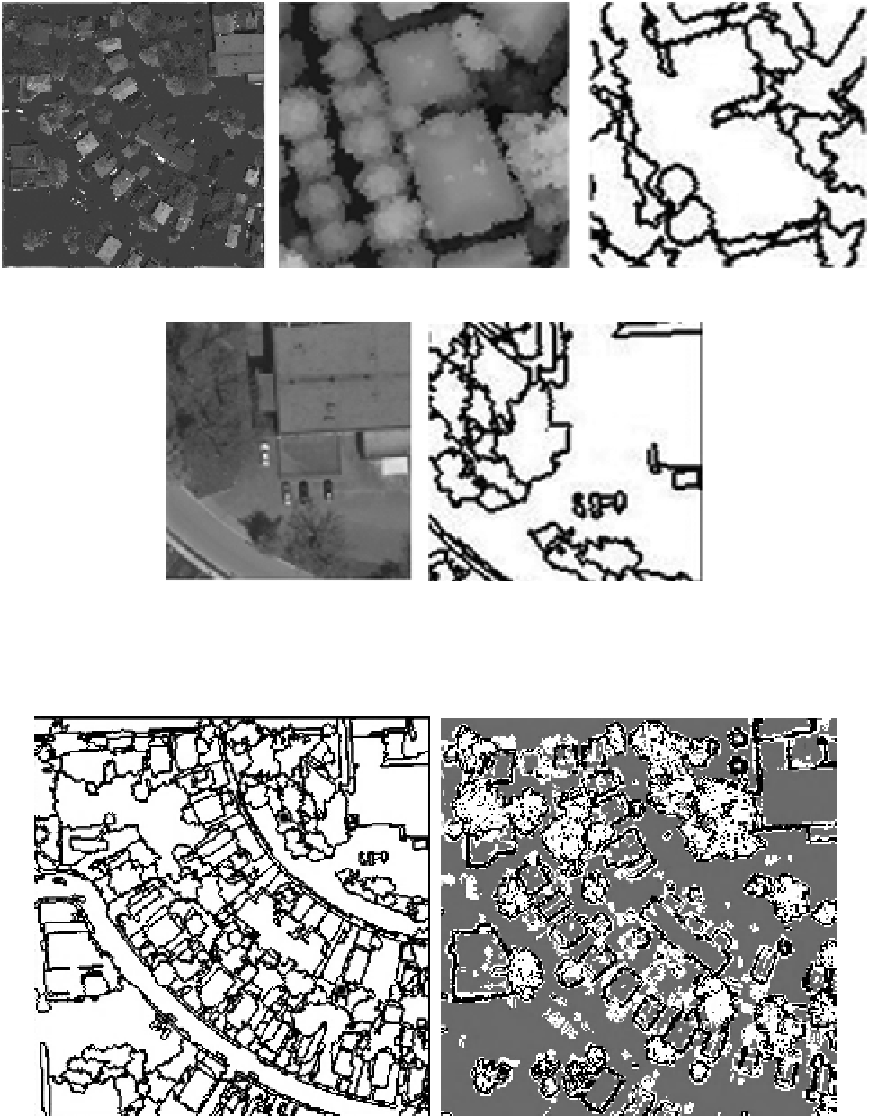
to that of the road. Figure 6.12(b) shows the materials of the
building and ground are similar, so they will always be partitioned
into a homogenous region in Fig. 6.12(c). However, the quality
of segmentation is not guaranteed when the range image (see
Fig. 6.12d) is used alone. For instance, if a tree is close to a
building, it is very difficult to separate one fromanother, as shown
in Fig. 6.12(e). Therefore, height information from lidar data as
an additional channel can improve the quality of color image
segmentation. Figure 6.13(a) shows the result of segmentation
by fusing lidar data and the aerial image. Figure 6.13(b) presents
the spatial discrete measurement result of lidar data by eigen-
analysis, in which most of tree regions are described as ''discrete''
and ''edges,'' while majority of building regions are presented as
''planes.''
Some parameters for the supervised object-oriented classifica-
tion need to be predetermined. First, the parameters of the prior
probability can be derived from the typical training set. The most
important parameters in this study are theweights of features. The
(a)
(b)
(c)
(e)
(d)
FIGURE 6.12
(a) Filtered result overlaid on the aerial image, (b) aerial image and (c) its corresponding segmentation results,
(d) lidar range image and (e) its corresponding segmentation results.
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 6.13
(a) The segmentation result of the aerial image fused with the height and texture information from lidar data;
(b) The spatial distribution result of lidar data by eigen-analysis.











Search WWH ::

Custom Search