Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
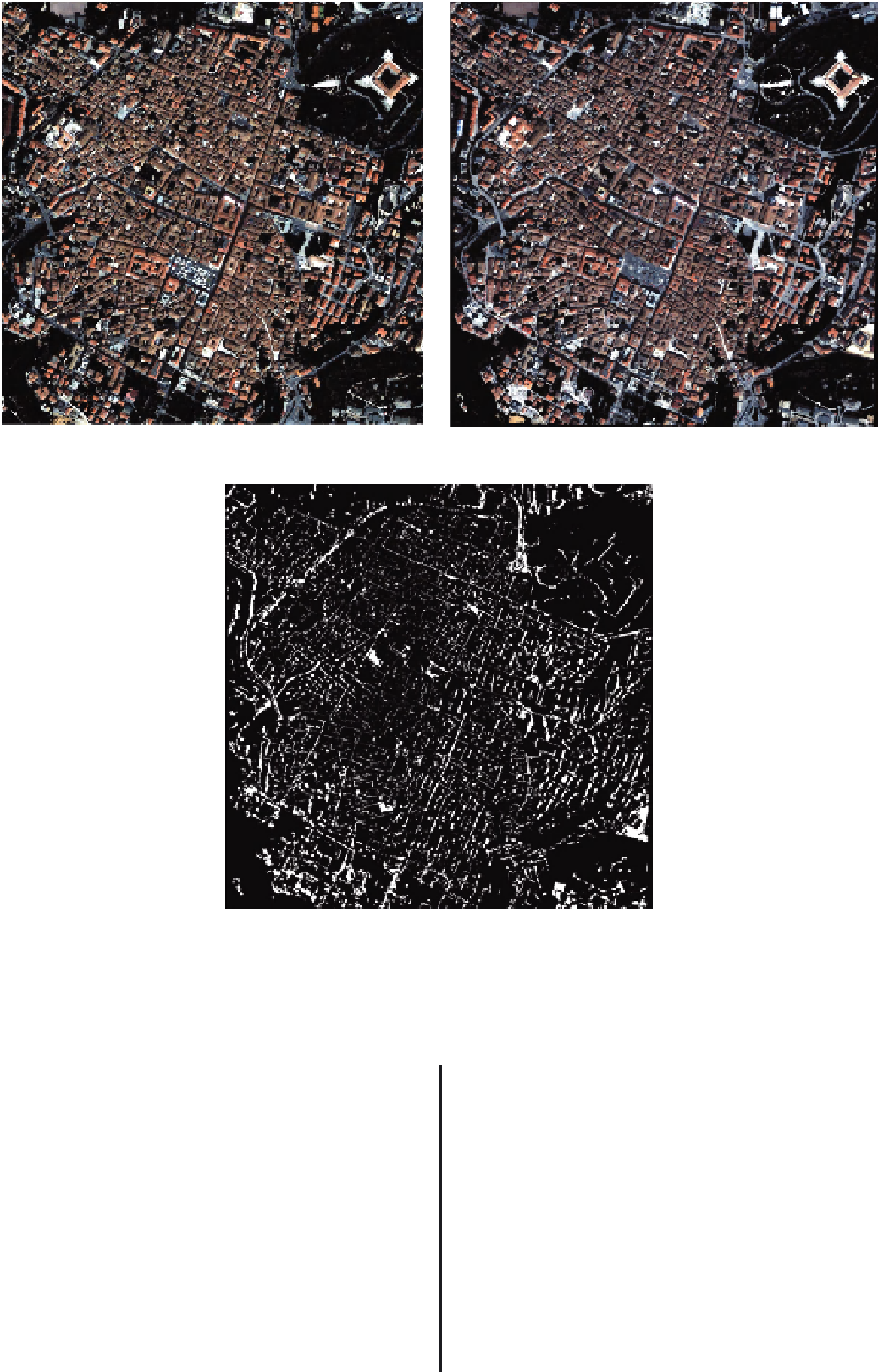
(a)
(b)
(c)
FIGURE 3.2
A small sample of two Quickbird images over L'Aquila in central Italy: (a) and (b) multitemporal VHR optical
dataset over the city centre; (c) change detection through post-classification comparison of the pixels belonging to the
''building'' class.
whenitsoriginisplacedatx:
●
Geodesic dilation. The geodesic dilation of size 1 of themarker
image
X
with respect to amask image
Y
with the same domain,
and such as
X
≤
Y
,isdefinedasthepoint-wiseminimum
between the mask and the elementary dilation of the marker:
ε
B
(
X
)
={
x
|
B
x
⊆
X
}
(3.1)
●
Dilation. The dilation of a set
X
by a structuring element
B
is defined as the locus of points
x
such that
B
hits
X
when its
origin coincides with
x
:
δ
(1
Y
(
X
)
=
δ
(1)
(
X
)
∧
Y
(3.3)
δ
B
(
X
)
={
x
|
B
x
∩
X
=}
(3.2)
●
Geodesic erosion. The geodesic erosion is the dual transforma-
tion of geodesic dilationwith respect to set complementation:
Morphological transformations involve combinations of one
input image with specific structuring elements (or SEs). The
approach for geodesic transformations is to consider two input
images, so that a morphological transformation is applied to
the first image, which must remain greater or lower than the
second one.
ε
Y
(
X
)
=
ε
(1)
(
X
)
∨
Y
(3.4)
Reconstruction by dilation. The reconstruction by dilation of
amaskimage
Y
from a marker image
X
is defined as the
●









Search WWH ::

Custom Search