Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
and to achieve bioconjugation the phenyl group must be converted into a
phenolic side chain. The introduction of the hydroxyl group increases the
nucleophilicity dramatically. The p
of the phenolic hydroxyl lies at 9.7-10.1
(Aslam & Dent, 1999; Hermanson, 1996).
Bioconjugation techniques utilizing Tyr side chains can be considered as
more advanced. Commercial reagents are typically not available; thus, the
starting materials and coupling reagents must be chemically synthesized.
The most common reaction utilizing Tyr side chains on VNPs is diazonium
coupling, which has been widely used on MS2 and TMV. One-electron oxidation
and modification of Tyr side chains on CPMV have also been reported
(see below).
K
a
.1..1
diazonium coupling
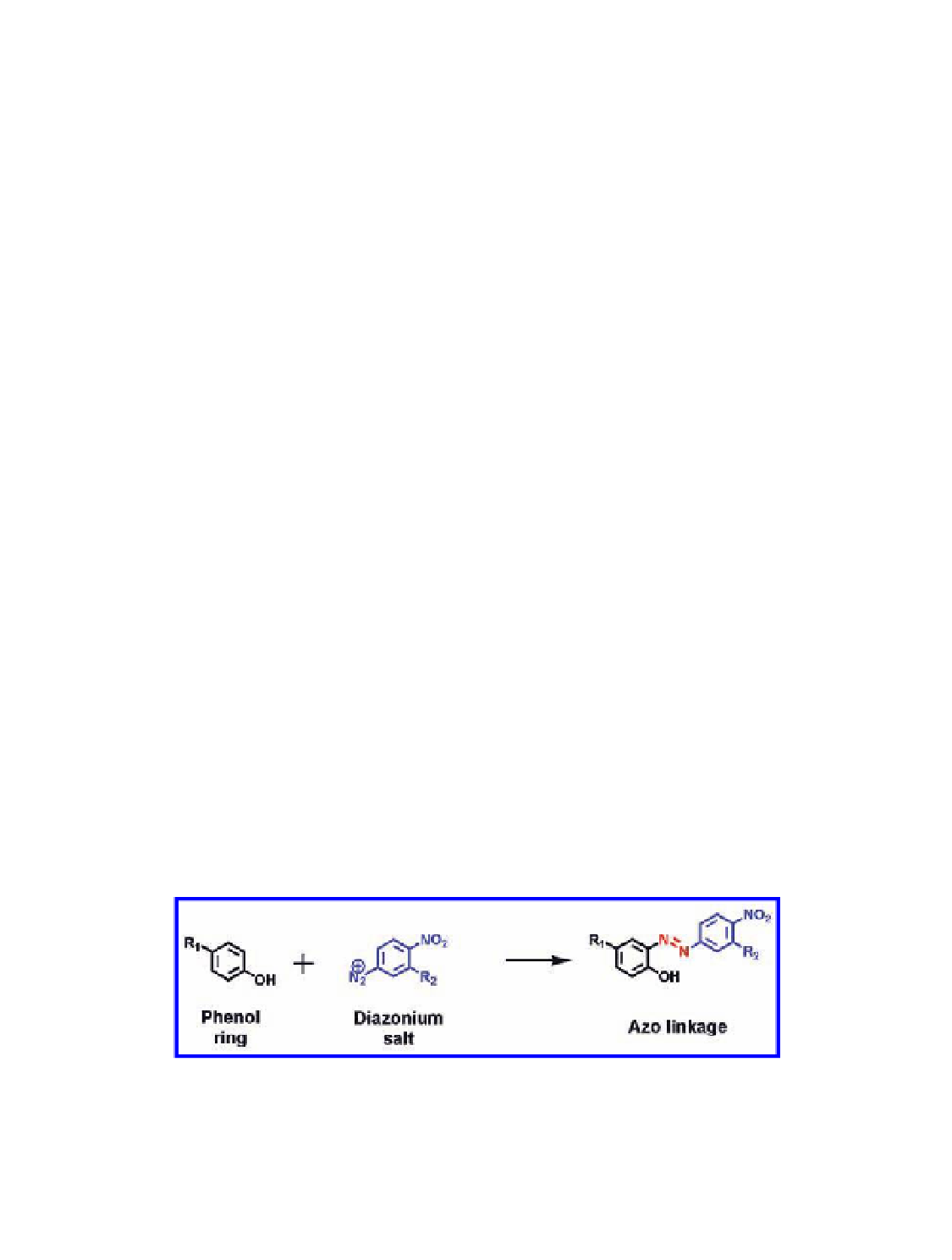
Diazonium coupling or azo coupling is the bioconjugation between an
aniline (typically aromatic) and a Tyr side chain. The highly electron-
deficient diazonium salt of the
-nitroaniline is widely used as a coupling
reagent. Coupling results in the installation of an azo linkage
p
to the
phenolic moiety of the Tyr side chain (Fig. 4.4). Francis and coworkers
(University of California Berkeley, CA, USA) have made great progress in
developing this coupling strategy for MS2 and TMV (Kovacs
ortho
et al.
, 2007;
Schlick
, 2005). Introduction of a functional group to the VNP is
achieved by using an aniline-containing derivative of the molecule of interest
(Kovacs
et al.
, 2007). Functionalized aniline compounds are typically not
commercially available and must be chemically synthesized. Alternatively,
an alkyne-containing aniline can be attached; the alkyne can be regarded
as
et al.
a
ligation
handle
for
subsequent
coupling
reactions
using
click
chemistry (Bruckman
, 2008) (see Section 4.1.2). Azo coupling has also
been used to introduce aldehyde functionalities into the VNP scaffold; the
aldehyde can serve as a target for oxime condensation reactions (Datta
et al.
et
al.
, 2008; Hooker
et al.
, 2007, 2008; Kovacs
et al.
, 2007; Schlick
et al.
, 2005)
(see Section 4.2.2).
Figure 4.4
-
nitroaniline; coupling results in a stable azo linkage. Figure provided by courtesy of
Vu Hong (TSRI, La Jolla, CA, USA).
Bioconjugation of Tyr side chains using a diazonium salt of the
p

Search WWH ::

Custom Search