Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
filename
The name of a file containing WKT, PROJ.4 strings, or XML/GML coordinate
system definitions can be provided.
3.2 Single and Multi-band Images
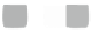
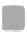
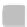
For single band raster images there is only one value assigned to each pixel. The
values can represent two distinct types of data: continuous fields (e.g. represented as
floating points) and categorical maps with a discrete number of classes (e.g. a land
cover map). The greyscale image in Fig.
3.3
a is an example of a continuous field that
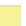
represents a digital elevation model (heights). The binary mask (0 or 1) in Fig.
3.3
b
and the land cover map in Fig.
3.3
c are examples of categorical maps.
The distinction of continuous fields and categorical maps is important when deal-
fields can be interpolated to meaningful values. For categorical maps, however, inter-
polation can lead to meaningless values that fall between two categories.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Fig. 3.3
Examples of single band raster images,
a
greyscale image,
b
binary mask,
c
landcover
map with three classes
Fig. 3.4
Example of multi-band image






























































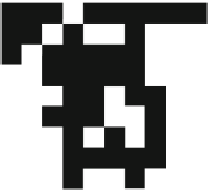


















































































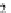

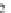



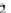














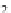
























































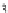





























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search