Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 3.1
Schematic overview of raster image using image coordinates
surface and defined by the geodetic datum. For practical reasons, for instance to sim-
plify geometric calculations, geodetic coordinates are often transformed to a (plane)
map projection, based on the same datum. Pixel locations are then described by
their (X,Y) coordinates in a projected coordinate system (see Fig.
3.2
). The con-
version to a plane can not be performed without distortion though (known as the
Gauss' Theorema Egregium).
3
Therefore, different map projections are constructed
to control the characteristics of the distortion and preserve some basic metric prop-
erty (conformality, distance, direction, scale, area). Each map projection corresponds
to a set of parameters that are used to transform the geodetic coordinates to plane
coordinates. For a mathematical background on map projections, we refer to other
textbooks (Bugayevskiy and Snyder 1995).
3
Gauss, Karl Friedrich. General investigations of curved surfaces of 1825, 1827 and 1902.









































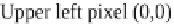








Search WWH ::

Custom Search