Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Geometry Column = ST_Centroid (geometry)
SUM(ST_Area (geometry)): Real (0.0)
OGRFeature (SELECT): 0
SUM(ST_Area (geometry)) (Real) = 0.252206490693434
POINT (3.116159337389504 48.94748608019286)
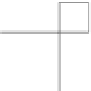
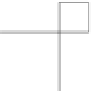
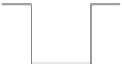
Vector spatial analysis typically includes merging, clipping and intersecting vec-
tors to generate new sets of data. These geometric intersections are illustrated in
Fig.
2.2
. Some of these methods can be done using
ogr2ogr
, while others can be
implemented using OGR and/or the GEOS library. We demonstrate some examples
using
ogr2ogr
.
Clipping
can be used to create a vector subset of the features using either the
spatial extent or another vector dataset.
Merging
multiple shapefiles into one shape-
file is often required during geospatial analysis. For instance, multiple administrative
boundaries need to be combined into one file or multiple sets of points need to be































Search WWH ::

Custom Search