Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.1
Vector data model:
points
,
lines
and
polygons
(including nodes and vertices)
•
Apoint can be defined either in 2- or 3-dimensions. In 2-dimensions a point consists
of a single pair of coordinates that is dimensionless in terms of area and distance
and its attributes are stored for each point. In 3-dimensions, a point consists of
three coordinates: an x, y and z (height).
•
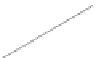
Lines are linear features that are represented by an ordered set of coordinate pairs.
Each line consists of line segments that run between adjacent coordinates in the
set. In some circumstances, the starting and ending points of a line are referred to
as nodes, while the intermediate points are termed vertices.
•
Polygons are areas that are formed by a set of bounding line segments. Each
polygon has an interior region that is bounded by its perimeter and this region can
also enclose other regions. Adjacent polygons can share common borders between
polygons. As is the case for the other vector features, attributes can be linked to
each polygon.
•
Multi-lines and multi-polygons are entities that contain several objects that are
grouped together to form one feature. For instance, many islands (multiple poly-
gons) are grouped together to form one island group.
•
Multi-linestrings are entities that consist of one to many linestrings.































Search WWH ::

Custom Search