Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
Height (m)
1000
1375
1750
2125
2500
0
500 1000 m
0
500 1000 m
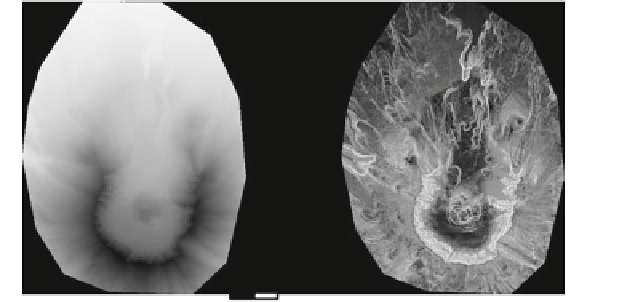
Fig. 10.6
Slope combined with relief mode applied to Mount St. Helens using
gdaldem
.
a
Digital
surface model.
b
Slope relief
degrees (e.g. Lat/Long WGS84 projection), you can use scale = 111120 if the
vertical units are meters (or scale = 370400 if they are in feet).
For the next example, we first calculate the slope of the DSMof Mount St. Helens.
The resulting is a floating point image where each pixel value represents the steep-
ness of the terrain in degrees. We then use
gdaldem
in
color-relief
mode
to generate a color relief map, using various shades of gray (shown in Fig.
10.6
).
The shades are automatically interpolated between the extreme values for 0
ⓦ
(flat
terrain is white) and 90
ⓦ
(steep terrain is black). For these two extreme values, we
provide the following color table as a text file (save these lines in
slope_ct.txt
).
0 255 255 255
90000
gdaldem slope st-helens_dsm_10m.tif st-helens_slope.tif
gdaldem color-relief st-helens_slope.tif slope_ct.txt
ₒ
st-helens_slope_relief.tif
10.6.3 Aspect
Aspect is an analysis mode that calculates the orientation (azimuth) of the slopes in
the DEM. Slopes can face North (0
ⓦ
), East (90
ⓦ
), South (180
ⓦ
), West (270
ⓦ
)orany
other direction in between. Instead of azimuth angles, a trigonometric angle can be




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search