Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
BL
complexity
Te m p o r a l
complexity
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
I/P
I/P
B0
BL
B1
B1
EL
Temporal level 0
i/p
i/p
Temporal level 1
b0
b1
Temporal level 2
b1
Temporal level 3
b2
b2
b2
b2
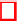
Fig. 6.
The use of information for combined scalability structure
Temporal
cor
for the current MB can be calculated from the mode complexity
and the motion vector of the previous temporal level at the corresponding MB
position. The estimated
Temporal
cor
is calculated by Eq. (4).
Temporal
cor
=
Temporal
complexity
MV
l−
1
val
=
Mode
l−
1
complexity
×
search size
,
(4)
where
l
is the temporal level as shown in Fig. 6.
Mode
complexity
indicates the
proposed mode number in Table 1. The value of
search size
represents the maxi-
mum length of search range.
MV
val
is defined by MV values in the corresponding
MB of the previous temporal level, which is expressed as
MV
val
=
avg
(
|
MV
x
|
+
|
MV
y
|
)
n
,
(5)
where
n
is the number of MV in the corresponding MB. The number of MV can
be various because partitioned ME is permitted in H.264/AVC. It is a integer
value by round up.
Quality
cor
·
Spatial
cor
is defined as
BL
complexity
, which represents the complex-
ity of texture in the base layer. For spatial scalability, the image in the base layer
and the image in the enhancement layer are very similar. However, the visual
quality between the base layer and the enhancement layer is extremely different,
which is affected by the different quantization scales. Therefore,
BL
complexity
is
calculated by
Quality
cor
·
Spatial
cor
=
BL
complexity
=
scale f actor
×
BL Mode
complexity
1
log
2
(
dif f QP
)
,
scale f actor
=
(6)
dif f QP
=
|
QP
BL
−
QP
EL
|
,
2
≤
dif f QP <
51
,



























Search WWH ::

Custom Search