Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
GOP size 4
Base
Layer
I/P
B1
B0
B1
I/P
High
Resolution
Inter layer prediction
i
b1
b0
b1
i/p
Enhancement
Layer
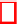
Fig. 1.
The structure of the spatial scalability with GOP size 4
GOP size 8
Prediction
I/P
B2
B1
B2
B0
B2
B1
B2
I/P
Key
picture
Key
picture
Fig. 2.
Bi-directional prediction for hierarchical B pictures
2.1 Type of Scalability
Spatial Scalability.
AsshowninFig.1,itgenerally starts with a base layer
at a lower resolution and adds an enhancement layer at higher resolution. The
input video source for base layer is preprocessed to create the lower resolution
image and is independently coded with H.264/AVC. In the enhancement layer
the difference between an interpolated version of the base layer and the source
image are coded. However, both base layer and enhancement layer have the same
frame rate and quality.
Quality Scalability.
Quality scalability maintains the same luminance resolu-
tion and frame rate in the lower layer and a single enhancement layer. However,
different quantization scales support the different qualities.
Temporal Scalability.
Temporal scalability, provided by the hierarchical B
picture structure, uses a technique to encode different temporal resolutions with
the same spatial resolution as shown in Fig. 2. The hierarchical B picture struc-
ture can be made using bi-directional motion prediction in the GOP. The bi-
directional motion search uses both forward reference pictures (list 0) and back-
ward reference pictures (list 1). As depicted in Fig. 2, the picture at the lowest


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search