Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
4
Experiments and Conclusion
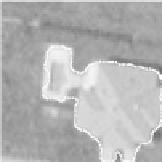
Some results of the contour detection can be seen in Figure 10.
The algorithm was tested for a few registered image pairs and the results were
promising. The algorithm was able to find almost every changed building and to
filter out non-changed ones.
The main advantage of our method is that it does not need any building tem-
plate and can detect objects of any size and shape. The method has diculties in
finding objects with similar colour to the background and sometimes one object
is described with more than one subgraphs. These problems need to be solved
in a forthcoming semantic or object evaluation step.
Harris characteristic function was used to determine changes between regis-
tered image pairs scanned with long time interval. The detected keypoint candi-
dates were then filtered and the number of remaining keypoints was enhanced by
saliency methods. A graph based representation was used to create initial contour
of changed objects, then GVF snake method generated the object boundaries.
Our experiments showed that saliency methods can be ecient tools when de-
termining changes. Our future works includes more evaluation and comparison
with other state-of-the-art algorithms.
Fig. 10.
Results of the contour detection by GVS snake method. The initial contour
was the convex hull of the vertices in the subgraph representing the object.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund under grant
number 76159. The authors would like to thank for the registered image pairs
to Hungarian Institute of Geodesy, Cartography and Remote Sensing (F OMI).





Search WWH ::

Custom Search