Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
a maximum value around noon and then decreased to reach its minimum value again around
18h. All treatments displayed the same development in leaf-water potential and stomatal
conductance. However, it is possible to observe:
•
The effect of salinity on the hourly values of leaf-water potential and of stomatal
conductance. The higher the salinity, the lower the leaf-water potential and stomatal
conductance.
•
The effect of the soil texture on the hourly values of leaf-water potential and of
stomatal conductance. Clay soil showed, in all treatments, lower values than loam
soil.
•
The differences observed are consistently significant in the case of the more saline
treatments (30 meq Cl/l).
3-2 Effect on Growth
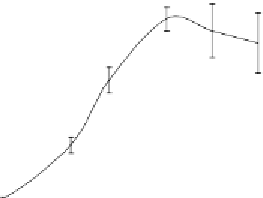
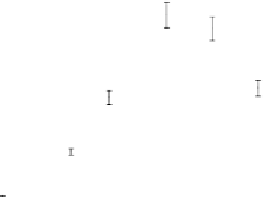
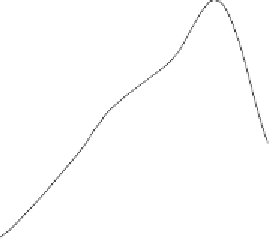
Figures 5 and 6 show the values per plant of leaf surface and the above-ground dry matter
observed for all treatments on the loam and clay soils.
loam
2400
1800
1200
600
C
15
30
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
clay
2400
1800
1200
600
C
15
30
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
D.A.S.
Figure 5. Values of leaf surface /plant observed during the soybean crop cycle on the loam and clay
soils for three water-quality treatments (control C, 15 and 30 meq/l).












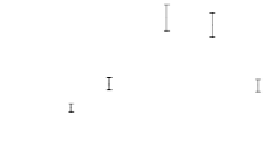







































Search WWH ::

Custom Search