Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
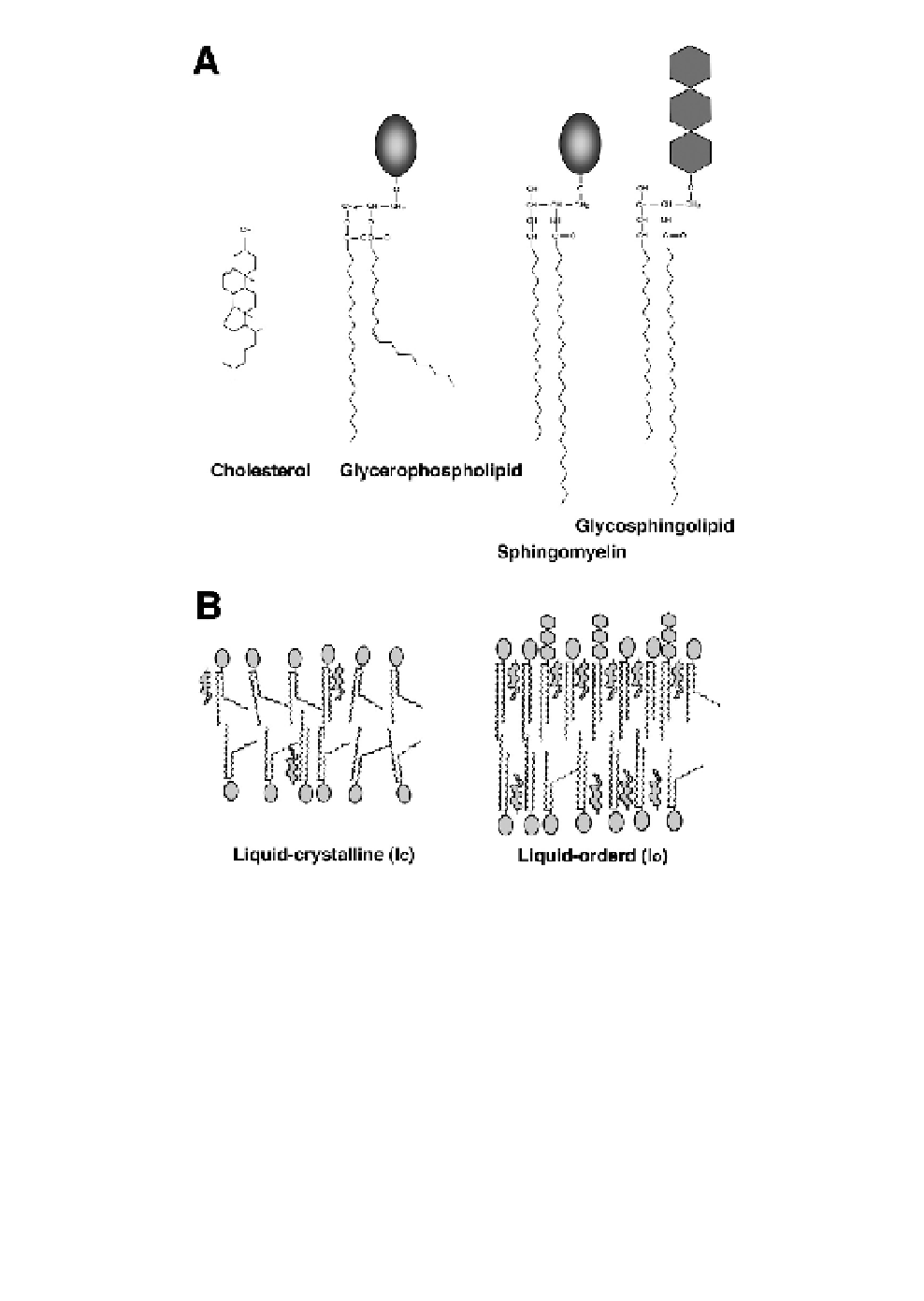
Fig. 1.
Lipid molecules of biological membranes and phases of the membrane
lipids. (
A
) The major classes of biological membrane lipids are phospholipids
(glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin), glycosphingolipids, and cholesterol.
Acyl chains of sphingolipids (sphingomyelin and glycosphingolipids) are satu-
rated, whereas an acyl chain of glycerophospholipids is usually kinked by a
cis
double bond (unsaturated). (
B
) Lipid bilayers composed predominantly of
glycerophospholipids are highly fluid as proposed by the fluid mosaic model,
1
where lipid molecules reside in a liquid-crystalline (lc) (or liquid-disordered)
phase. With cholesterol, sphingolipids become highly ordered but retain their
lateral and rotational mobility, residing in a liquid-ordered (lo) phase. Lipid
molecules of raft microdomains are thought to be in a lo or a lo-like phase.