Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
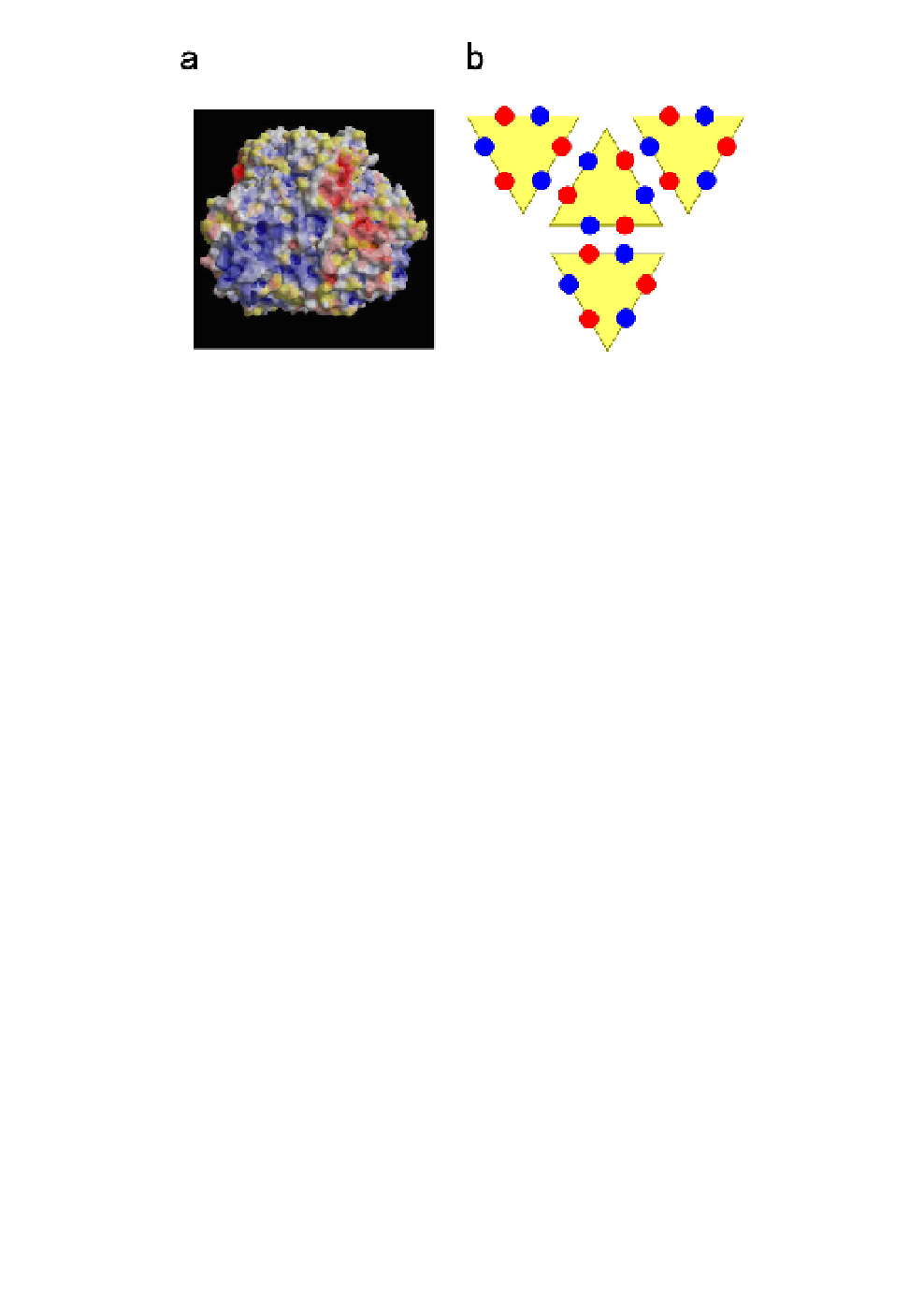
Fig. 9.
Interactions among P8-trimers.
2
(a)
Surface electrostatic potential
on a P8-trimer, as viewed from the interface between two P8-trimers.
Positively charged regions are colored blue and negatively charged regions
are colored red. Charged regions are clustered, suggesting that they might
complement the distribution of charges on neighboring P8-trimers. The
electrostatic potential map was calculated by the program used for the eF-site.
(b)
Schematic representation of side-by-side interactions among P8-trimers.
Positively charged patches (shown in blue) and negatively charged patches
(shown in red) make electrostatic pairs at the P8-P8 interfaces.
amino acid residues 274 through 276. This region includes a unique
amino acid sequence, namely, a glycine triplet (GGG). The second and
third glycine residues are especially close to corresponding residues
related by icosahedral two-fold symmetry. A bulky side chain at this
position, even a methyl group, might result in steric hindrance of the
interactions between P8-trimers. This triplet is semiconserved in viruses
that belong to the genus
Phytoreovirus
, such as RGDV
19
and
Wound
tumor virus
(WTV),
20
which have SGG and AGG triplets, respectively.
Thus, the bilateral features in the atomic structure of P8-trimers might
be significant for the interactions that allow self-assembly of the viral
outer capsid.
A transcapsidation study was performed to confirm this hypoth-
esis.
21
Three-dimensional homology mapping of P8-trimers indicated
that the amino acid residues involved in the interaction between the
edges of P8-trimers are strongly conserved (Fig. 7), as is the case for