Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Other Computational Strategies for Design
of Immunogens
Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs)
“Evolutionary algorithm” is a generic term that groups three inde-
pendently developed computational problem-solving methods:
genetic algorithms (GA), evolutionary strategies (ES), and evolution-
ary programming (EP). These three methods are biologically inspired
by the principles of Darwinian evolution, but differ in the implemen-
tation of these principles. In general, all three methods include treat-
ment of proposed possible solutions as members of a population that
are varied for fitness (or adaptation) to their environment. Members
of the population are subjected to selection pressures, and the sur-
vivors (parents) breed offspring (children) by the application of
genetic operations such as mutation, crossover (recombination), or
both. These operations proceed in a cyclical manner for a number of
user-defined generations, after which fitter population members have
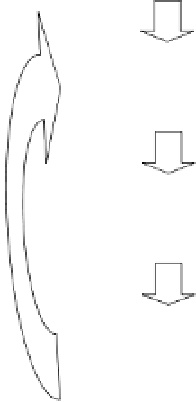
evolved from the original population as seen in Fig. 4.
Original Population of
Starting Solutions
Original Population of
Starting Solutions
Select Fit Population
Members
Select Fit Population
Members
Breed New Problem
Solutions
Breed New Problem
Solutions
Generate Next
Generation Population
Generate Next
Generation Population
Fig. 4.
General scheme used by EAs for problem solving.