Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
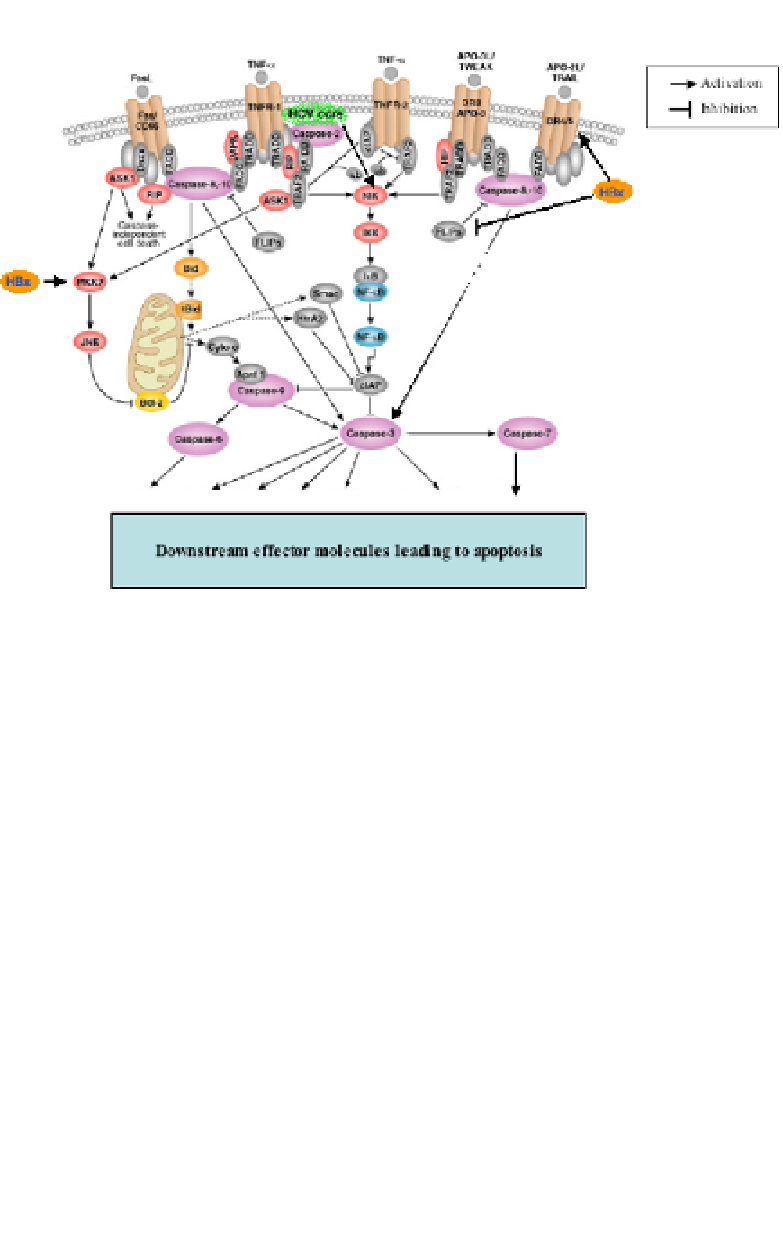
Fig. 4.
Apoptosis pathways and their regulation by hepatitis viruses.
B
activity in HCV core-expressing cells.
77
Signaling through TNFR is
variable and highly controversial, ranging from being protective,
irrelevant or pro-apoptotic. The outcome of the signal is decided by
the stimulus and the cell type. While HCV can cause apoptotic death
by signaling through TNFR, it may also overcome the TNF-medi-
ated death pathway by activation of NF
to controls.
76
Further, mobility shift assays also showed higher NF
κ
B (Fig. 4) and contribute to
viral persistence and hepatocarcinogenesis.
76,77
The anti-apoptotic
effects of the HCV core protein probably account for a chronically
activated and persistent state in HCV infected cells, leading to hepa-
tocarcinogenesis. The role of TNFR and Fas signaling in hepatitis B
is generally linked to sensitization of HBV-infected hepatocytes to
TNF or Fas ligand. The HBx protein was shown to induce apopto-
sis by prolonged stimulation of the stress-mediated MEKK1 path-
way
78
and by up-regulating expression of the TRAIL receptor DR5.
79
It was also shown to bind to the cellular FLICE inhibitor protein
κ